Figure 1.
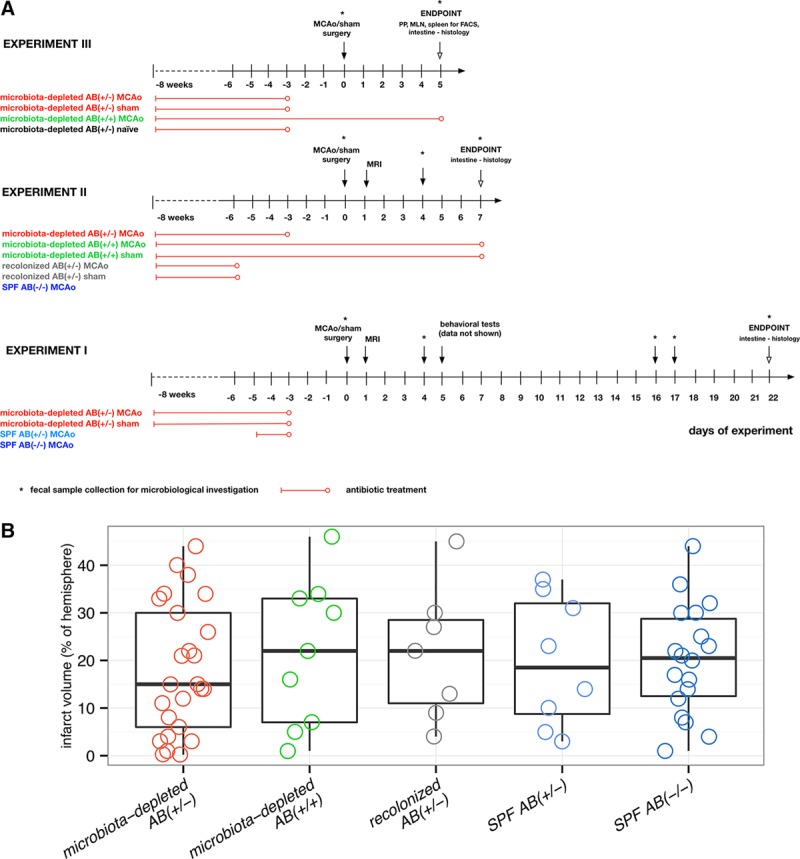
Experimental setup and infarct volume. A, Experimental setup (3 independent experiments). Experimental groups: microbiota-depleted AB(+/−) MCAo/sham, with antibiotic treatment stopped 72 h before surgery; microbiota-depleted AB(+/+) MCAo/sham, with antibiotic treatment during the entire experiment; recolonized AB(+/−) MCAo/sham, microbiota-depleted mice recolonized with SPF microbiota; antibiotic treatment was stopped 48 h before recolonization; microbiota-depleted AB(+/−) naïve, microbiota-depleted animals without any surgical intervention with antibiotic cocktail stopped 72 h before the experiment; SPF AB(−/−) MCAo, conventionally colonized (specific pathogen-free microbiota) mice without any antibiotic treatment, subjected to MCAo surgery; SPF AB(+/−) MCAo, SPF mice with antibiotic treatment for 48 h up to 72 h before surgery. B, Infarct volume assessed by MRI at day one after MCAo did not differ between investigated groups. Microbiota-depleted AB(+/−) n=25, microbiota-depleted AB(+/+) n=9, recolonized AB(+/−) (microbiota-depleted recolonized with SPF microbiota) n=7, SPF AB(+/−) (SPF with antibiotic treatment for 48 h) n=8, SPF AB(−/−) n=18. Box plot with whiskers minimum to maximum. No statistically significant differences were found when comparing all experimental groups (Kruskal Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc) or when comparing microbiota-depleted AB(+/−) with SPF AB(−/−) mice Mann–Whitney test). FACS indicates flow cytometric analysis; MCAo, middle cerebral artery occlusion; MLN, mesenteric lymph nodes; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PP, Peyer’s patches; and SPF, specific pathogen-free.
