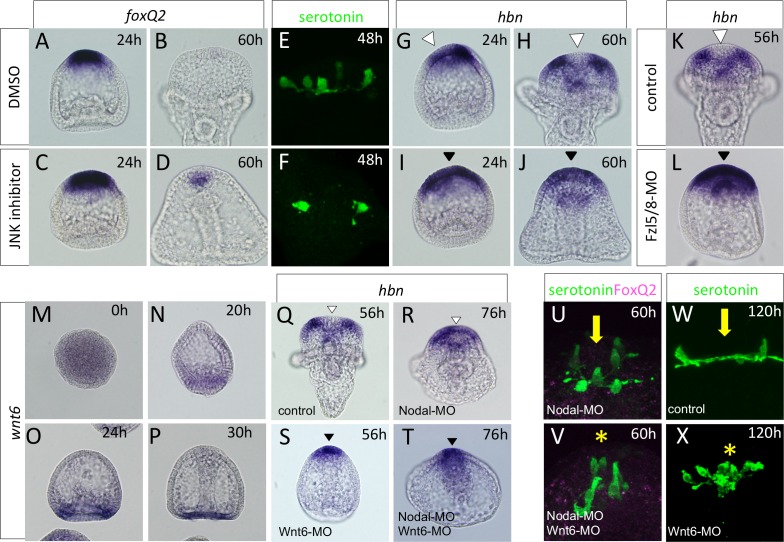
Fig 7. Wnt6 is a ligand for non-cWnt pathway that regulates the patterning of hbn expression.
(A, C) foxQ2 expression in the control (DMSO-treated) and JNK inhibitor treated embryos at 24 h. (B, D) foxQ2 expression in the control (B) and in JNK inhibitor treated embryo (D) at 60 h. A trace level of foxQ2 was expressed in JNK inhibitor treated embryos, whereas foxQ2 is completely diminished in the control at this stage. (E, F) The serotonergic neurons are differentiated at 48 h with or without JNK function. The AP region is magnified. (G-J) hbn clearance does not occur in JNK inhibitor-treated embryos. (K, L) hbn remains at the anterior end of AP in Fzl5/8 morphants at 56 h. (M-P) wnt6 was strongly expressed in the veg2 endoderm region at 20 h, and afterward it was maintained in the vegetal plate until at least 30 h. (Q, S) hbn does not disappear from the anterior end and is not expressed in the non-AP region in Wnt6 morphants, and this is independent of the presence or absence of Nodal (R, T). (U-X) Without Wnt6 function, serotonergic neurons are differentiated at the anterior end of the AP. To visualize the phenotype more clearly during early stages, Nodal-MO was simultaneously injected. Arrow in (U, W) indicates the anterior end that misses serotonergic neurons. Asterisk in (V, X) shows that the serotonergic neurons are present at the central part of AP. White and black arrowheads indicate the location of hbn absence and presence, respectively.