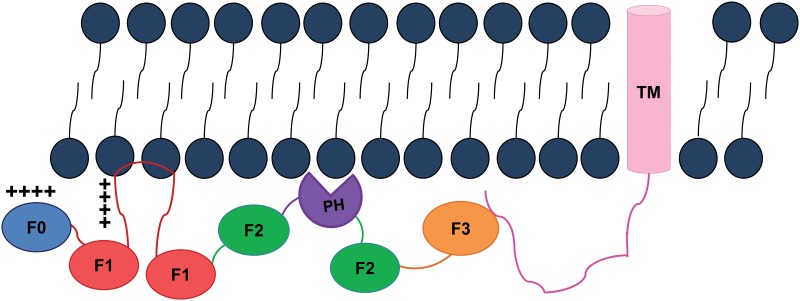
Fig 6. Localization of the FERM domain of kindlin in membrane.
A hypothetical cartoon showing proximity of the FERM domain of kindlin to the lipid membrane and interactions with the beta cytosolic tail. The FERM domain interacts with the phospholipid lipid bilayer (shown as black stick with round head) through F0 subdomain (in blue), PH (in purple) and potentially with split F2 (in green) and F3 (in pink) subdomains by ionic interactions with exposed positively charged surface. The unfolded F1 loop of the F1 subdomain (in red) might insert into the lipid membrane using N-terminal positive charged residues of poly-lys and sidechain of hydrophobic residues. Such a membrane localization of the FERM domain of kindlin might bring the F3 subdomain for optimal interactions with the beta cytosolic tail attached with its TM (in light purple) for activation of integrins.