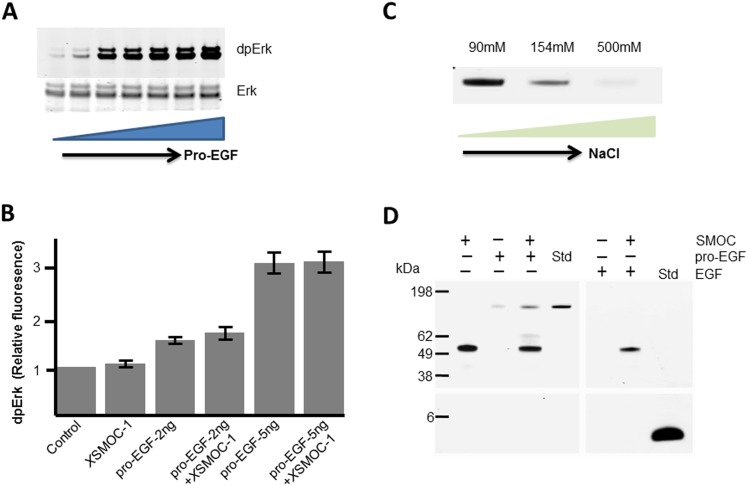
Fig 4. XSMOC-1 does not potentiate MAPK signaling by pro-EGF, but can bind to pro-EGF when bound to heparin sepharose.
(A) Immunoblot of 32D/EGFR cell lysates showing Erk phosphorylation (dpErk) following a six minute exposure to a dilution series (0–500ng/ml) of pro-EGF. Total Erk is shown as loading control. (B) Graph showing relative dpErk fluorescence obtained on immunoblots from triplicate experiments of 32D/EGFR cells following a six minute exposure to submaximal concentrations of pro-EGF (2ng or 5ng/ml) in the presence or absence of XSMOC-1 (100μg/ml).The level of dpErk by pro-EGF was not significantly affected by XSMOC-1. (C) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE showing the heparin sepharose (HS) elution profile of pro-EGF in the presence of increasing concentrations of NaCl (D) Coomasie-stained SDS-PAGE showing HS elution profiles (±) following incubation of 5μg XSMOC-1 with 5μg of either pro-EGF or EGF in PBS/500mM NaCl, compared to each protein alone. A standard (std) lane is provided for pro-EGF and EGF to demonstrate their expected migration position.