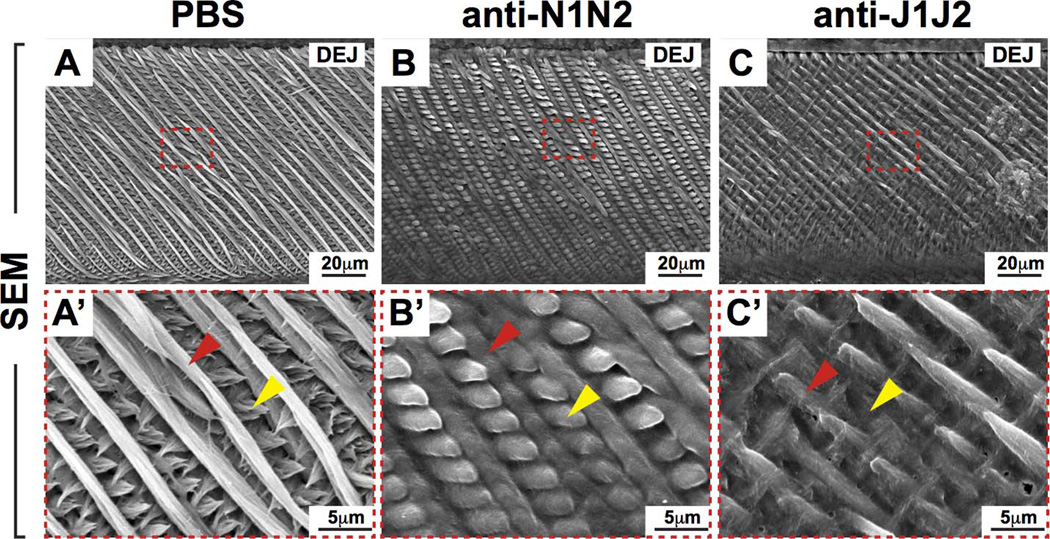
Figure 6. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of adult mouse incisors.
(A–C) SEM analysis of incisor enamel in mice treated with PBS or Notch antibodies in sagittal views. (A’–C’) Magnified views of red-boxed regions (A–C). Red arrowheads point to primary enamel rods and yellow arrowheads point to inter-rod enamel. Note the enlarged inter-rod enamel in anti-N1N2 incisors (B,B') compared to controls. In anti-J1J2 incisors, note the interrupted primary rod enamel and smaller size of inter-rod enamel (C,C') compared to controls. These observations highlight distinct roles of N1N2 and J1J2 in incisor enamel formation. DEJ, dentin-enamel junction; N1, NOTCH1; N2, NOTCH2; J1, JAG1; J2, JAG2.