Abstract
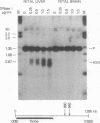
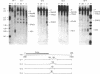
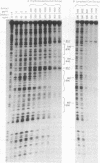
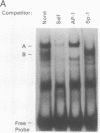
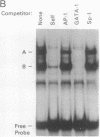
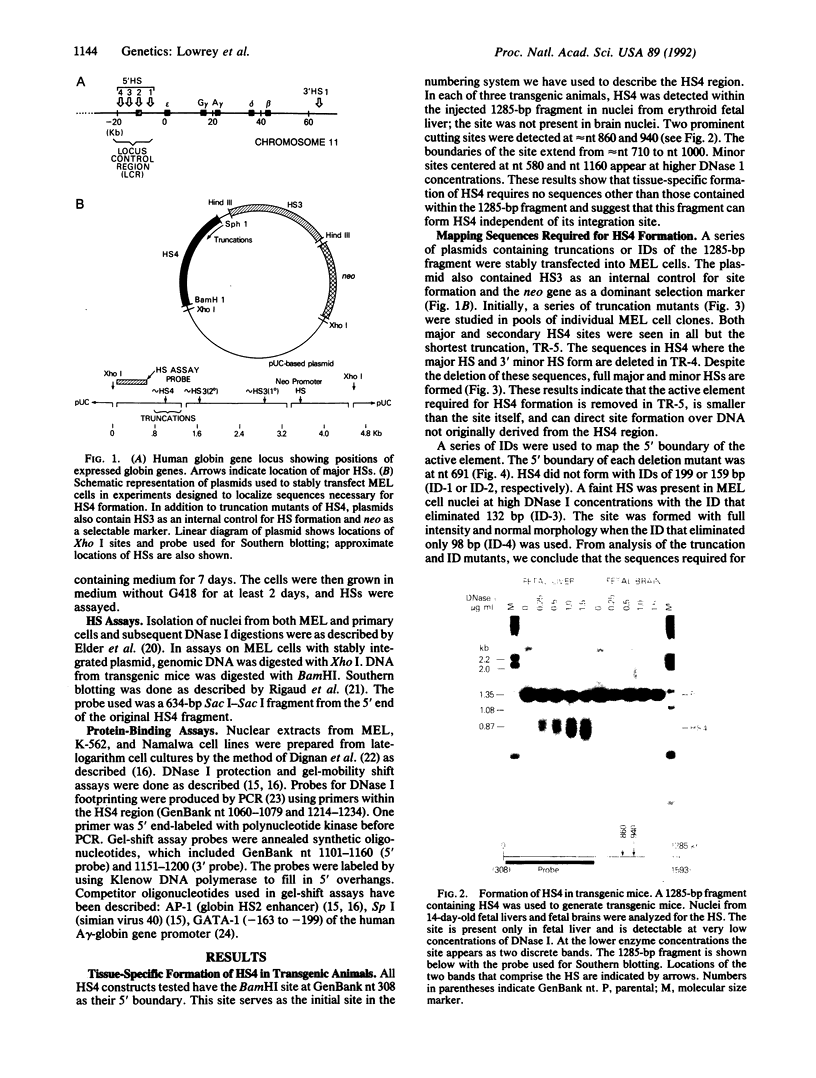
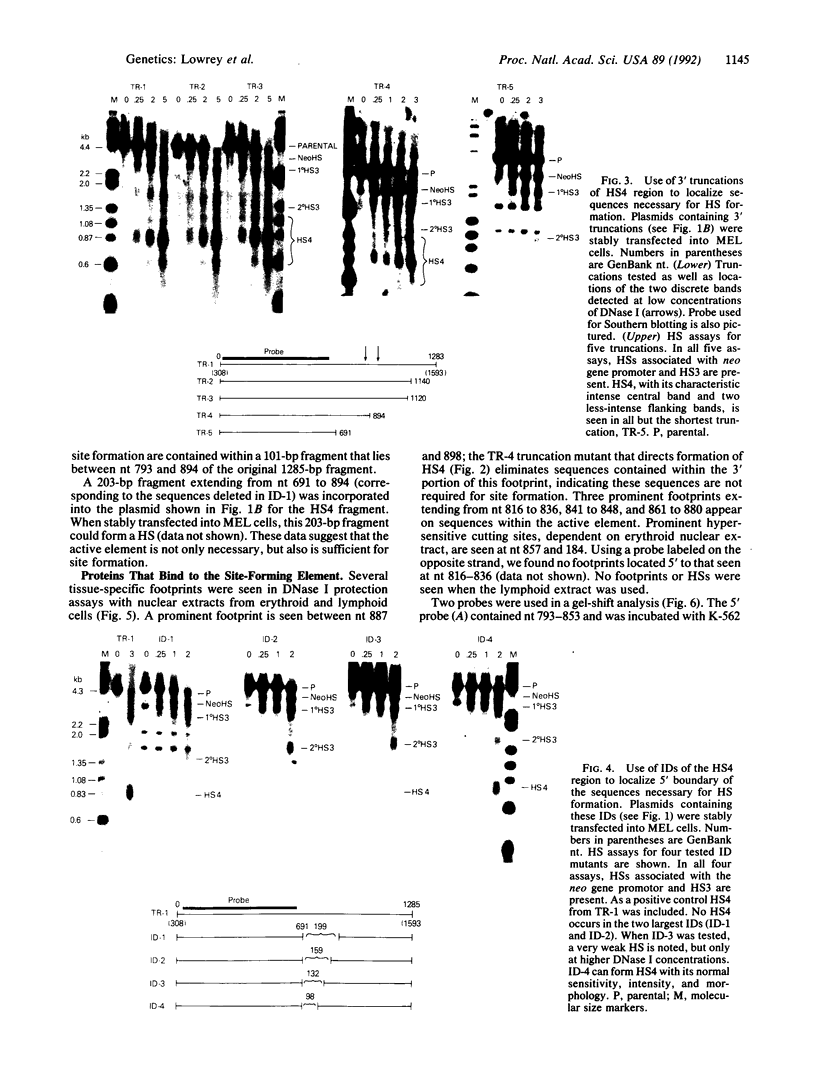
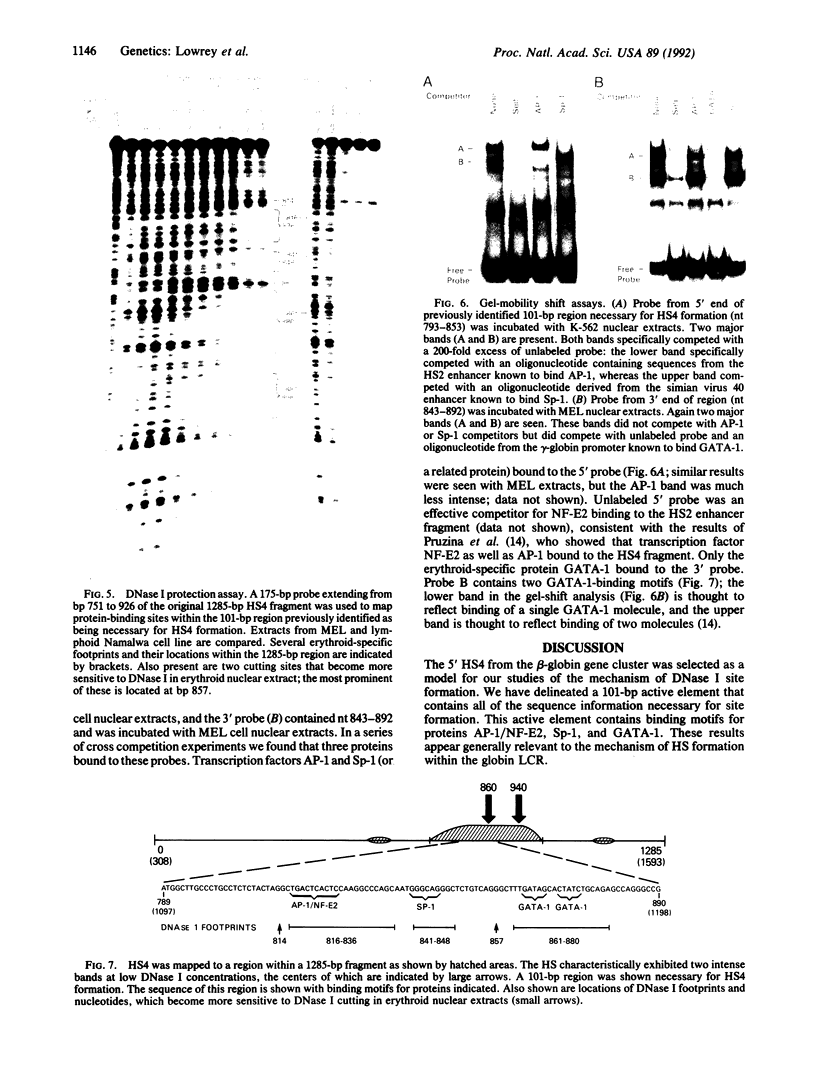
The human beta-like globin gene locus contains embryonic, fetal, and adult globin genes that are regulated in a developmentally timed, as well as a tissue-specific, manner. The locus control region (LCR), located 5' of the globin genes, is characterized by four erythroid-specific nuclease-hypersensitive sites within native chromatin. These sites contain the active elements of the LCR. The LCR establishes an active chromatin conformation across the globin locus and enhances globin gene expression in transfected erythroleukemia cells and transgenic mice. We have used 5' DNase I hypersensitive site (HS) 4 as a model to define the minimum elements necessary for site formation. We have identified a 101-base-pair fragment within 5' HS4 that is the active site-forming element. DNase I footprint and gel-mobility shift assays have identified binding sites for transcription factors AP-1/NF-E2, Sp-1, and GATA-1 within the HS-forming element. We conclude that HS formation, the characteristic feature of the LCR in nuclear chromatin, requires interaction between erythroid-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P. T., Kan Y. W. The inactive beta globin gene on a gamma delta beta thalassemia chromosome has a normal structure and functions normally in vitro. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):766–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll M. C., Dobkin C. S., Alter B. P. Gamma delta beta-thalassemia due to a de novo mutation deleting the 5' beta-globin gene activation-region hypersensitive sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7470–7474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Forrester W. C., Thompson C., Mager D., Henthorn P., Peretz M., Papayannopoulou T., Groudine M. Translocation of an erythroid-specific hypersensitive site in deletion-type hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1382–1389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Nickol J. M., Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. Analysis of the tissue-specific enhancer at the 3' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4786–4790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Epner E., Driscoll M. C., Enver T., Brice M., Papayannopoulou T., Groudine M. A deletion of the human beta-globin locus activation region causes a major alteration in chromatin structure and replication across the entire beta-globin locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1637–1649. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Thompson C., Elder J. T., Groudine M. A developmentally stable chromatin structure in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T. Human fetal to adult hemoglobin switching: changes in chromatin structure of the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Vanin E., deLange T., Flavell R. A., Grosveld F. G. Beta-globin gene inactivation by DNA translocation in gamma beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):662–666. doi: 10.1038/306662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh K. T., Lin H. J., Lowrey C. H., Bodine D. M., Nienhuis A. W. The upstream region of the human gamma-globin gene promoter. Identification and functional analysis of nuclear protein binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11965–11974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ney P. A., Sorrentino B. P., Lowrey C. H., Nienhuis A. W. Inducibility of the HS II enhancer depends on binding of an erythroid specific nuclear protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6011–6017. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ney P. A., Sorrentino B. P., McDonagh K. T., Nienhuis A. W. Tandem AP-1-binding sites within the human beta-globin dominant control region function as an inducible enhancer in erythroid cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):993–1006. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Talbot D., Fraser P., Grosveld F. The beta-globin dominant control region: hypersensitive site 2. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2159–2167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzina S., Hanscombe O., Whyatt D., Grosveld F., Philipsen S. Hypersensitive site 4 of the human beta globin locus control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1413–1419. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Lee E., Westphal H., Felsenfeld G. Site-independent expression of the chicken beta A-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):749–752. doi: 10.1038/348749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Grange T., Pictet R. The use of NaOH as transfer solution of DNA onto nylon membrane decreases the hybridization efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):857–857. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Martin N. C., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A single erythroid-specific DNase I super-hypersensitive site activates high levels of human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):314–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino B., Ney P., Bodine D., Nienhius A. W. A 46 base pair enhancer sequence within the locus activating region is required for induced expression of the gamma-globin gene during erythroid differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2721–2731. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Grosveld F. The 5'HS2 of the globin locus control region enhances transcription through the interaction of a multimeric complex binding at two functionally distinct NF-E2 binding sites. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1391–1398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Philipsen S., Fraser P., Grosveld F. Detailed analysis of the site 3 region of the human beta-globin dominant control region. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2169–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taramelli R., Kioussis D., Vanin E., Bartram K., Groffen J., Hurst J., Grosveld F. G. Gamma delta beta-thalassaemias 1 and 2 are the result of a 100 kbp deletion in the human beta-globin cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7017–7029. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]