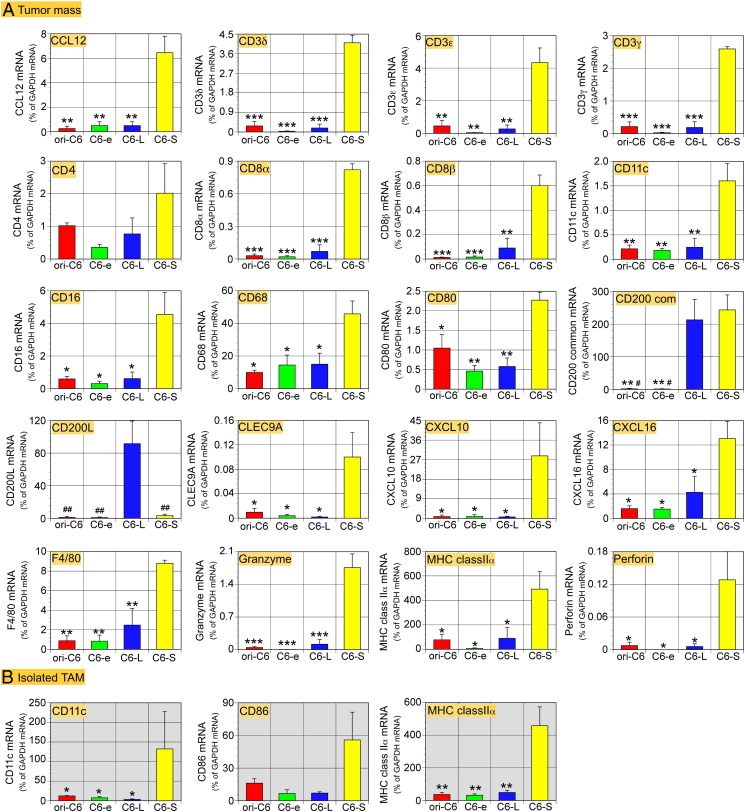
Figure 7.
Expression levels in tumors and isolated TAMs of mRNA encoding molecules related to CD200, DCs, lymphocytes and T cells, as revealed by qPCR. Data are shown in an alphabetical order. (A) cDNA was prepared from tumor masses dissected out 21 days after transplantation. CD200-mRNA amplified with ‘CD200 com’ primers was highly expressed by C6-L and C6-S tumors, whereas the CD200L-mRNA level was high only in the C6-L-tumors. The C6-S-tumors expressed DC markers, MHC class II α, CD11c, and CD80 at significantly higher levels than other tumors. Expression of mRNA encoding lymphocyte markers CD8α and β, CTL-related apoptosis-inducing molecules, granzyme, and perforin was significantly higher in the C6-S tumors. Despite not showing statistical significance, CD4 and IFNγ-mRNA were also highly expressed in the C6-S tumors. CLEC9A, which is expressed by myeloid DCs and responsible for cross-presentation, and chemokines (CCL12, CXCL10 and CXCL16), which are invovlved in recruitment of monocytes and lymphocytes, are also highly expressed in the C6-S tumor. (B) Shortly after isolation from the tumor mass, TAMs were subjected to qPCR analysis. TAMs from the C6-S-tumors expressed MHC class II α-, and CD11c-mRNA was expressed at significantly higher levels than in TAMs from other tumors. CD86-mRNA expression in TAMs from the C6-S tumors was also high. Data from 3 tumors of each cell lines are expressed as means ± SEM. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 versus CD200S; #P < .05, ##P < .01 versus CD200L.