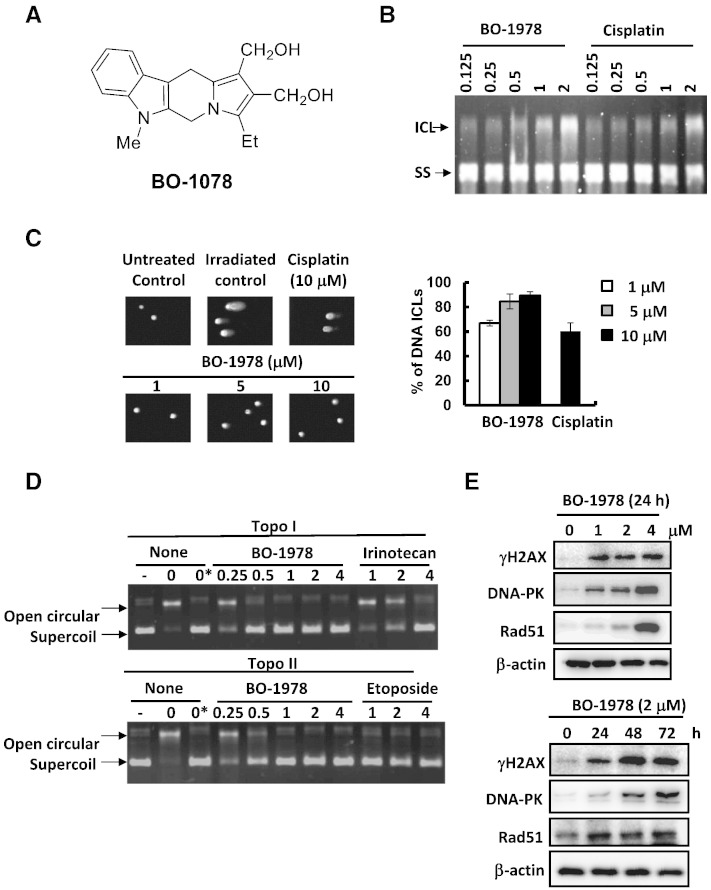
Figure 1.
DNA damage induced by BO-1978. (A) Chemical structure of BO-1978. (B) Formation of DNA cross-linking by BO-1978. Plasmid DNA was treated with various concentrations (0.125 to 2 μM) of BO-1978 or cisplatin for 2 hours at 37°C. The ICL and single-strand DNA was electrophoretically separated under alkaline conditions, as described in the Materials and Methods section. (C) Induction of DNA ICLs in H460 cells by BO-1978. H460 cells were treated with various concentrations (1, 5, and 10 μM) of BO-1978 or 10 μM cisplatin for 2 hours. DNA ICLs formed in H460 cells were identified using a modified comet assay. (D) Inhibition of intracellular topo I (upper panel) and II (lower panel) activities in H460 cells. The nuclear extracts of BO-1978–treated H460 cells (0.25 to 4 μM for 72 hours) were prepared and incubated with pEGFP-N1 plasmid DNA and specific topo I or topo II buffer for 30 minutes at 37°C as described in the Materials and Methods section. The relaxation of plasmid DNA was analyzed by electrophoresis. Irinotecan and etoposide served as positive controls for topo I and topo II, respectively. (E) The DNA damage response of H460 cells to BO-1978. H460 cells were treated with BO-1978 at the concentrations of 1 to 4 μM for 24 hours or 2 μM BO-1978 for various time periods (24 to 72 hours). γH2AX (Ser139), DNA-PK, and Rad51 protein expression levels were determined by western blotting.