Figure 4.
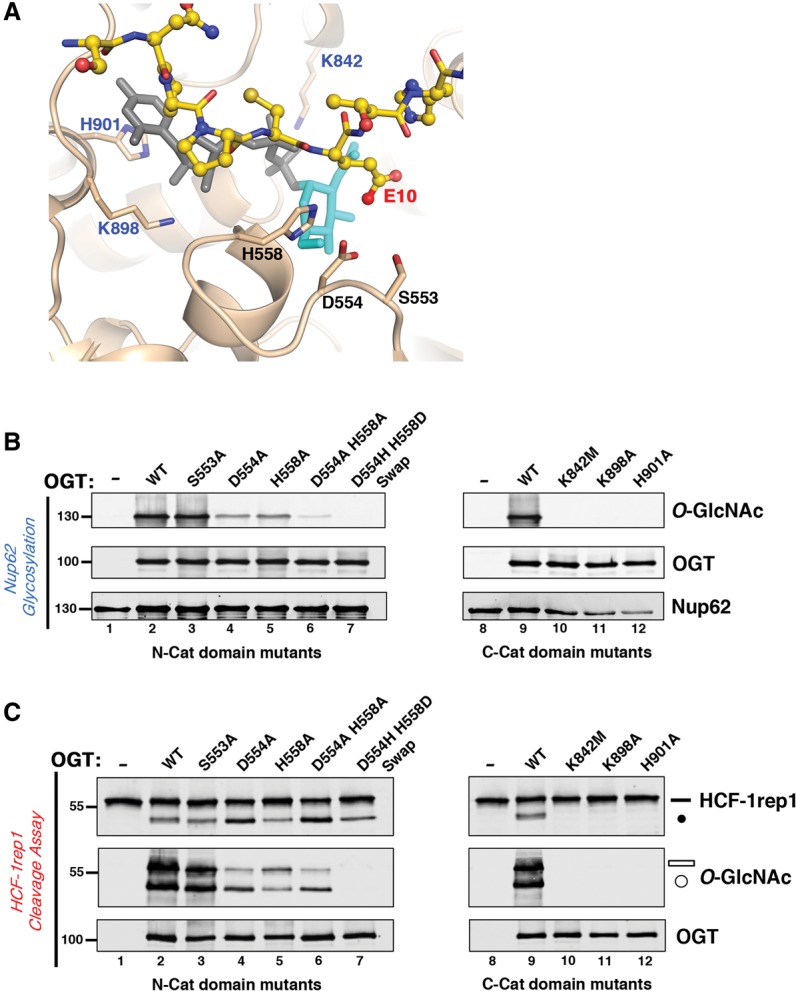
A glycosylation-defective OGT is effective for HCF-1 proteolysis. (A) Close-up view of the HCF-1PRO repeat 2 cleavage region (yellow), with E10 (labeled in red) interacting with the UDP-GlcNAc-bound (gray–turquoise) OGT Cat domain (tan). N-Cat domain residues S553, D554, and H558 are labeled in black, whereas C-Cat domain residues K842, K898, and H901 that interact with the UDP-GlcNAc molecule are labeled in blue. (B) OGT N-Cat (lanes 3–7) and C-Cat (lanes 10–12) domain mutants were incubated with Nup62 to assay glycosylation activities. Anti-O-GlcNAc RL2 antibody was used to detect Nup62 glycosylation, whereas anti-OGT and anti-Nup62 antibodies were used to detect OGT and Nup62 protein levels, respectively. (C) HCF-1rep1 substrate was incubated with either wild-type or OGT N-Cat (lanes 3–7) or C-Cat (lanes 10–12) domain mutants for in vitro HCF-1rep1 cleavage and glycosylation assay. HCF-1rep1 cleavage and glycosylation were detected with anti-GST and anti-O-GlcNAc RL2 antibodies, respectively. Anti-OGT was used to detect OGT protein. (Black bar) Uncleaved HCF-1rep1 substrate; (black circle) cleaved product; (white bar) glycosylated uncleaved HCF-1rep1 substrate; (white circle) glycosylated cleaved product.
