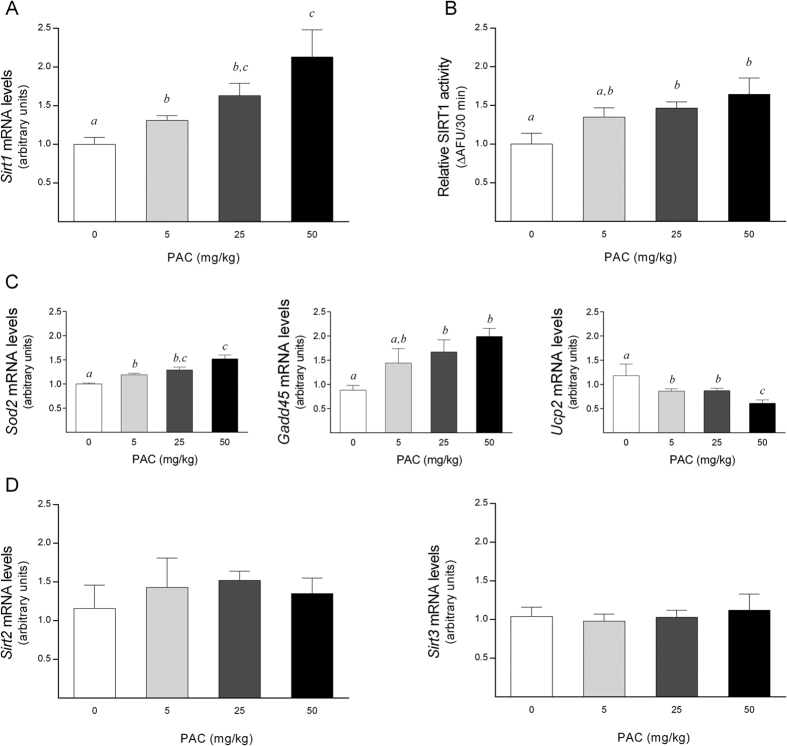
Figure 5. Hepatic SIRT activity in healthy rats supplemented with different doses of PACs.
(A,B) PAC consumption dose-dependently increased the hepatic Sirt1 mRNA levels (A) and SIRT1 activity (B). (C) The mRNA levels of Gadd45 and Sod2 were significantly up-regulated in a dose-dependent manner, whereas the Ucp2 mRNA levels were down-regulated in a similar manner. (D) There was no statistically significant effect of PAC consumption on the hepatic Sirt2 or Sirt3 mRNA levels. SIRT activity was indirectly assessed by determining both the mRNA levels of Sirt1, Sirt2 and Sirt3 and the mRNA levels of selected specific genes modulated by FOXO1 activity. The mRNA levels of the selected genes were normalized to the Ppia mRNA levels. The animals were fed a standard chow diet supplemented with 0 (control group), 5, 25 or 50 mg of PACs/kg bw for 21 days. The values shown are the means ± SE of 10 animals per group. The letters denote a significant difference between groups (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA). AFU: arbitrary fluorescence units; Gadd45: growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45; PACs: proanthocyanidins; Sirt: sirtuin; Sod2: superoxide dismutase 2; Ucp2: uncoupling protein 2.