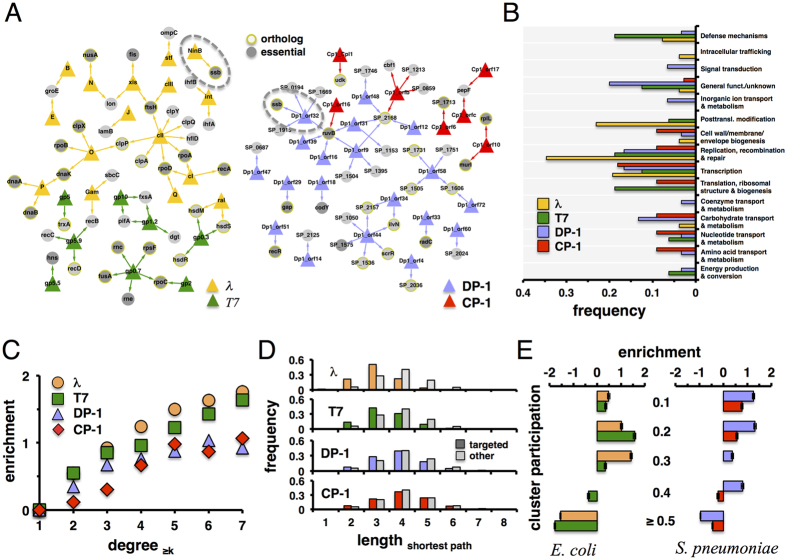
Figure 1. Comparison of the host-phage interaction interface of lambda and T7 with E. coli and Dp-1 and Cp-1 with S. pneumoniae.
In (A) we collected 36 protein-protein interactions between 16 lambda and 23 E. coli proteins as well as 19 interactions between 8 T7 and 14 E. coli proteins from the literature. In turn, we found 11 interactions between 7 Cp-1 and 10 proteins of S. pneumoniae, while we determined 38 interactions between 19 Dp-1 and 24 proteins of S. pneumoniae. In both host organisms we observed a limited number of proteins that were targeted by lambda and T7 (RecB, HsdM, HsdS) as well as Dp-1 and Cp-1 (RuvB, SP_2168). Furthermore, we observed that targets are frequently essential and have orthologs in the other organism. Notably, Ssb is evolutionarily conserved in both E. coli and S. pneumoniae and is targeted by lambda as well as Dp-1 (dashed circles). In (B) we determined the frequency of phage-targeted proteins and their functional classes. (C) Utilizing protein interactions in E. coli we observed that lambda and T7 targets appear to have an increasing number of interaction partners. Focusing on S. pneumoniae, we obtained similar results when we considered targets of bacteriophages Dp-1 and Cp-1. In (D) we calculated shortest paths from targeted proteins to all other host proteins in the corresponding host interaction networks of E. coli and S. pneumoniae. Comparing distributions that correspond to lambda and T7, we found that the lengths of shortest paths from targeted proteins are significantly shorter than paths from non-targeted proteins (Student’s t-test, P < 10−11). We obtain a similar result when we considered targets of phages Dp-1 and Cp1 (P < 10−12). In (E) we calculated the cluster participation coefficient of proteins that were targeted by bacteriophages of E. coli and S. pneumoniae. As a null model, we randomly sampled such sets of targeted proteins 10,000 times. Determining their enrichment, we observed that targeted proteins appear to predominantly reach into more complexes through their interactions than randomly expected. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Colors as in (B) and (C).