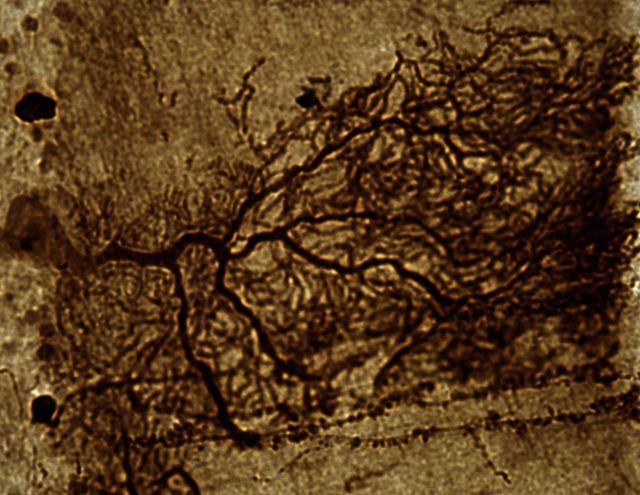
Adeno-associated viral delivery of a microRNA targeting ATXN1 provides therapeutic benefit in mouse models of spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Keiser et al. assess the translatability of this approach using adult rhesus macaques, and show that targeted delivery to deep cerebellar nuclei silences endogenous ATXN1 mRNA in multiple SCA1-affected sites.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.