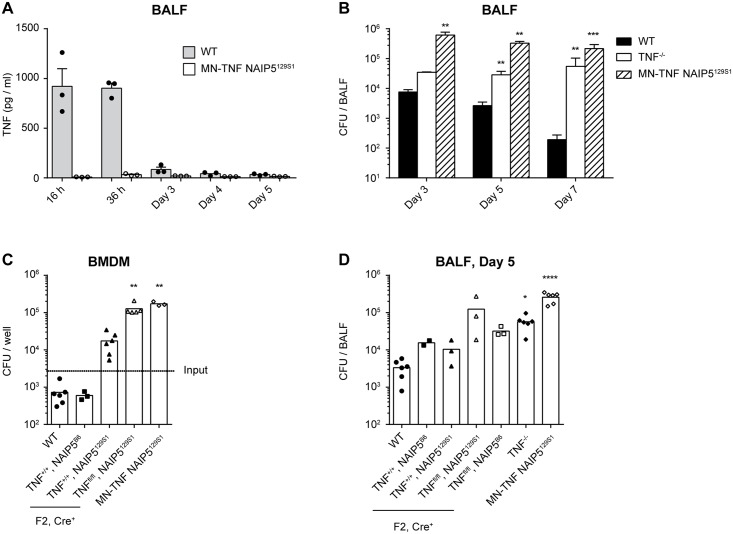
Fig 5. NAIP5129S1 and TNF-deficiency in macrophages, monocytes and neutrophils are the genetic traits that render MN-TNF NAIP5129S1 mice susceptible to L. pneumophila infection in vitro and in vivo.
(A-B) WT, TNF-/-, MN-TNF NAIP5129S1 mice were infected intranasally with WT L. pneumophila, and analyzed at the indicated time points. (A) TNF was quantified in the BALF via CBA assay. (B) BALF CFU were quantified on CYE agar plates. (C) WT or MN-TNF NAIP5129S1 BMDM, or BMDM from the F2 offspring of MN-TNF NAIP5129S1 x C57BL/6 intercrosses were infected with WT L. pneumophila at MOI 0.1. 3 days p.i. BMDM were lysed and CFU were quantified on CYE agar plates. (D) WT, TNF-/-, MN-TNF NAIP5129S1 mice, or the F2 offspring of MN-TNF NAIP5129S1 x C57BL/6 intercrosses were infected intranasally with WT L. pneumophila, and 5 days p.i. BALF CFU were quantified on CYE agar plates. All of the F2 offspring shown are Cre+. Panel A is from 1 experiment, panels B-D are from 2–3 pooled experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 compared to WT by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post test.