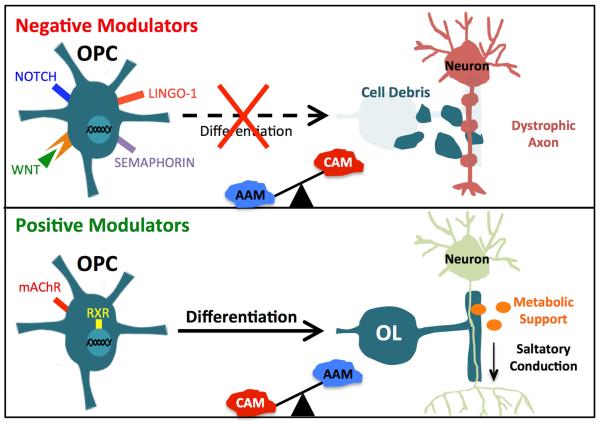
Figure 1.
Negative modulators of remyelination include Notch, Wnt, Lingo, and Semaphorin signaling as well as extracellular debris. Positive modulators of remyelination include muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) signaling. Remyelination efficiency is also dependent on extrinsic factors, including those secreted by classically activated (CAM) and alternatively activated (AAM) macrophages/microglia, and a balance between CAM and AAM appears to modulate the regenerative process. Since myelin is necessary for saltatory conduction and oligodendrocytes provide metabolic support to neurons, chronic demyelination and oligodendrocyte loss in MS are likely to contribute to axonal dystrophy and progressive neurodegeneration.