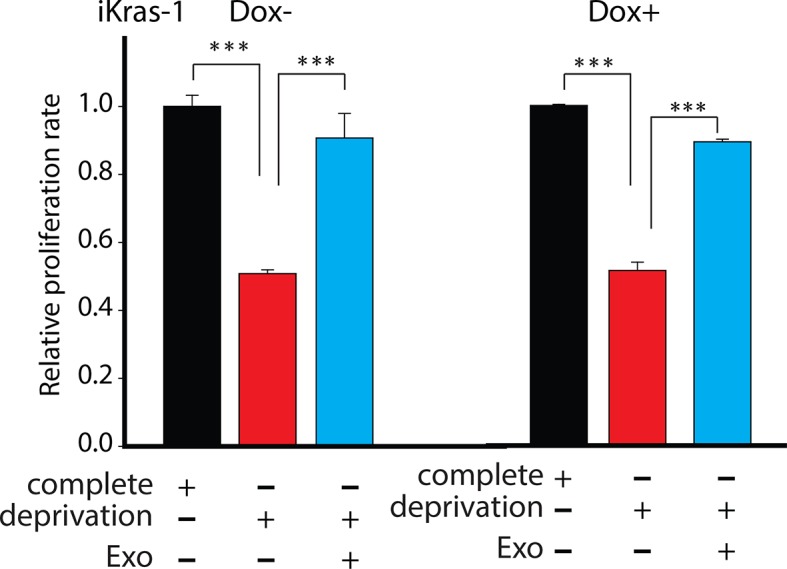
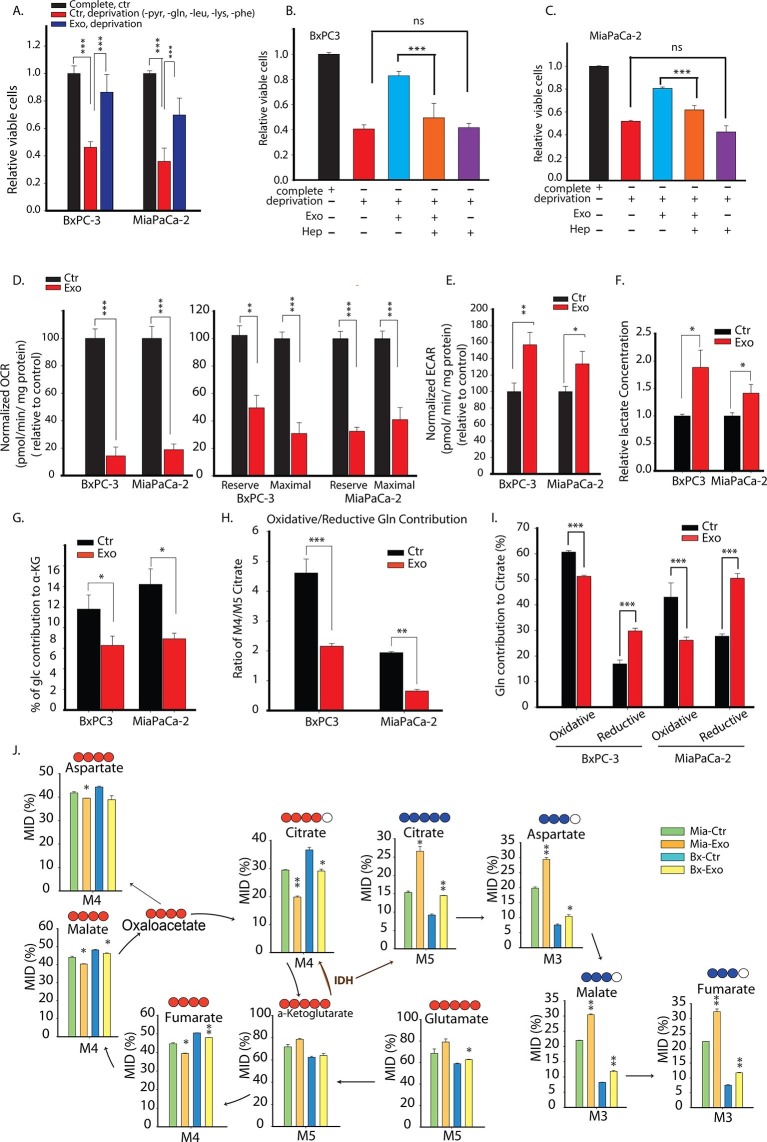
Figure 7. Pancreatic CDEs' metabolic reprogramming of pancreatic cancer cells is Kras independent.
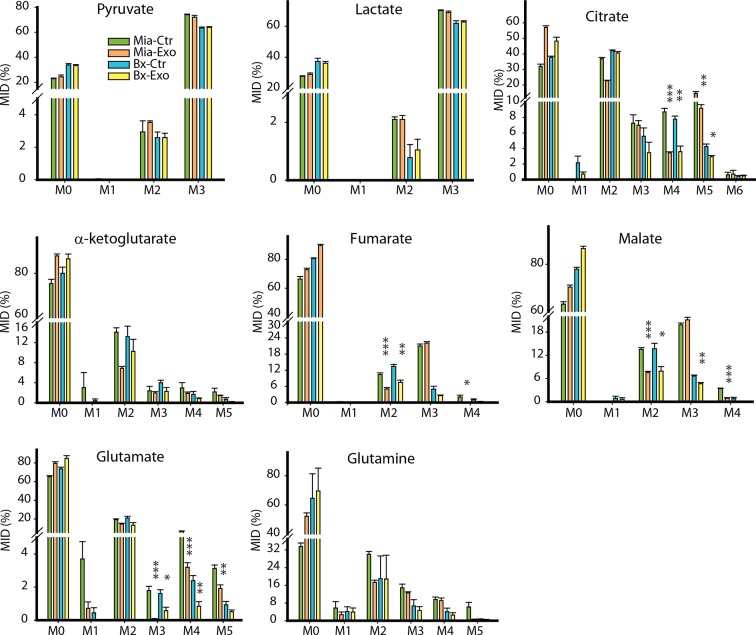
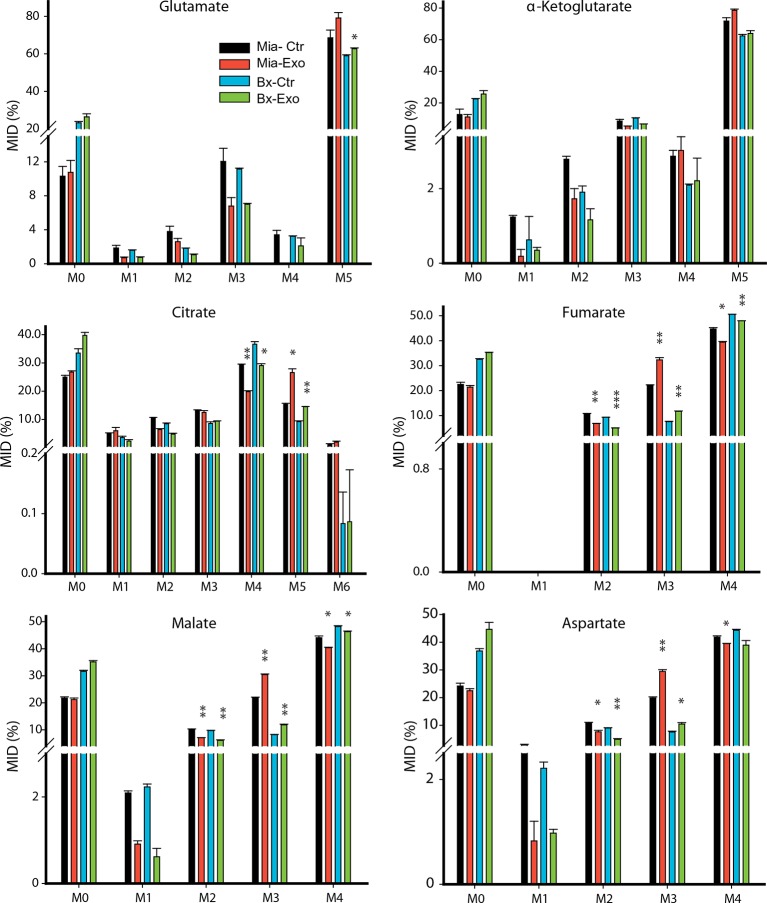
(A) Effect of pancreatic CDEs on pancreatic cancer cell viability under nutrient deprivation (without lys, phe, gln, pyr, leu) conditions. CDEs rescue loss of both wild-type and activated Kras expressing pancreatic cancer cells proliferation under deprivation conditions. Viability of cancer cells with and without exosomes in deprivation condition was measured after 48 hr (n=10). (B,C) Heparin inhibit exosomes uptake and thus inhibit the rescue of proliferation by exosomes under nutrient deprived conditions. Heparin (50μg/ml) disrupts receptor-mediated endocytosis. Before adding exosomes, heparin was added to wells for incubation for at least 0.5 hr (n=5). (D) Basal OCR were measured for BxPC3 and MiaPaCa-2, pancreatic cancer cell lines cultured with pancreatic CAFs (CAF19) exosomes. OCR of both BxPC3 and MiaPaCa-2 were downregulated by CAF19 exosomes. (n=10). Maximal OCR and reserve OCR of BxPC3 and MiaPaCa-2 were downregulated by CAF19 exosomes (n=10). (E) ECAR of both BxPC3 and MiaPaCa-2 were upregulated by CAF19 exosomes (n=10). (F) Relative lactate abundances were measured using GC-MS in BxPC3 and MiaPaCa-2 cells cultured with and without CAF19-secreted exosomes for 24 hr (n=4). (G) Percentage of glucose contribution to α-ketoglutarate in BxPC3 and MiaPaCa-2 cells with and without CAF19-secreted exosomes (n=4). (H) Pancreatic CDEs increased reductive glutamine metabolism in wild-type and activated Kras expressing pancreatic cancer cells. Oxidative contribution to citrate is determined by calculating M4 citrate percentage; reductive contribution to citrate is determined by M5 citrate percentage (n=4). (I) Ratio of oxidative to reductive glutamine contribution to citrate in wild-type and activated Kras expressing pancreatic cancer cells with CAF19-secreted exosomes (n=4). (J) Mass isotopologue distributions (MID) of glutamate, α-ketoglutarate, citrate, malate, and fumarate in BxPC3 and MiaPaCa-2 cancer cells cultured with and without CAF19-secreted exosomes in U-13C5 glutamine (n=4). Higher reductive glutamine metabolism is detected through higher M5 citrate, M3 fumarate, M3 malate, M3 aspartate in pancreatic cancer cells cultured in presence of exosomes. Reductive glutamine metabolism (n=4). Data information: data in (A) are expressed as mean ± SD, data in (B–J) are expressed as mean ± SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Figure 7—figure supplements 1–4.
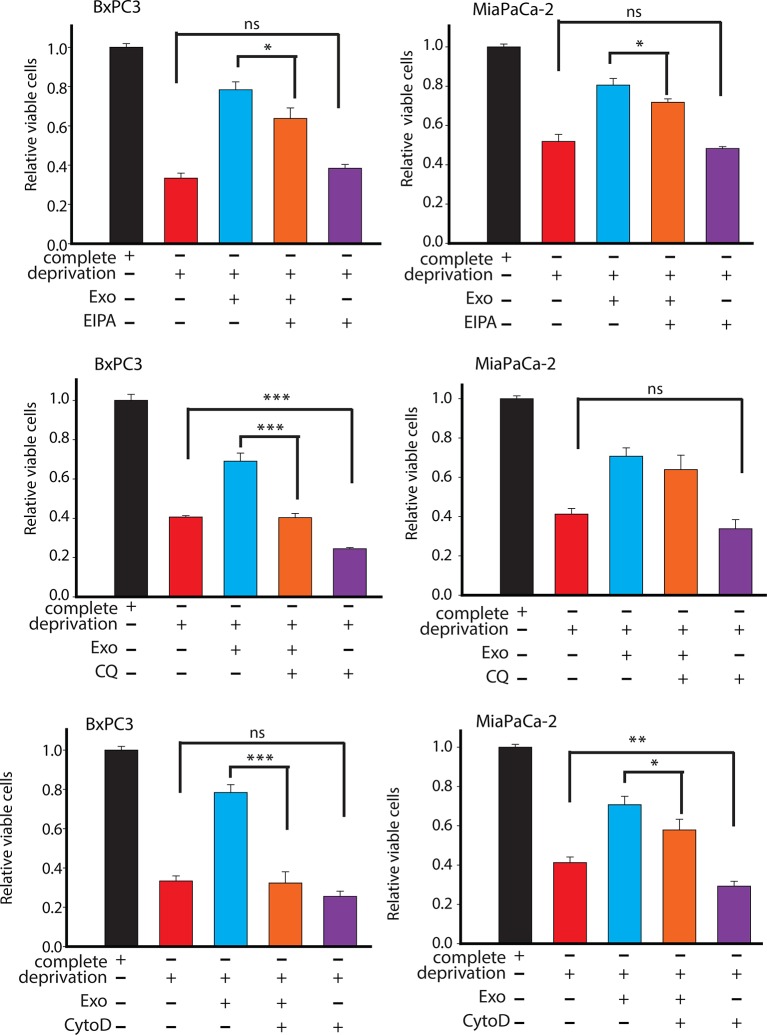
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Effect of drugs inhibiting CDEs uptake and utilization on BxPC3 or MiaPaCa-2 cell proliferation under deprivation (without lys, phe, gln, pyr, leu) conditions.
Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Effect of pancreatic CDEs on pancreatic cancer cell proliferation under nutrient deprivation (without lys, phe, gln, pyr, leu) conditions.