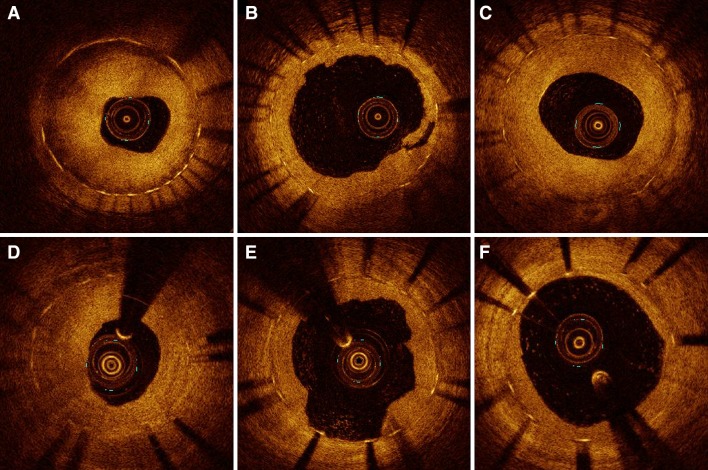
Fig. 1.
Illustrative OCT imaging of the same coronary segment for each time point (baseline, post-PCI and follow-up). Severe in-stent restenosis at baseline (a and d). After PCI, lumen enlargement with neointimal disruption and (micro) dissections are observed (b and e), caused by the mechanical effect of DEB angioplasty. Follow-up shows complete healing of the dissections with a moderate increase (C) and limited decrease in neointima (F)