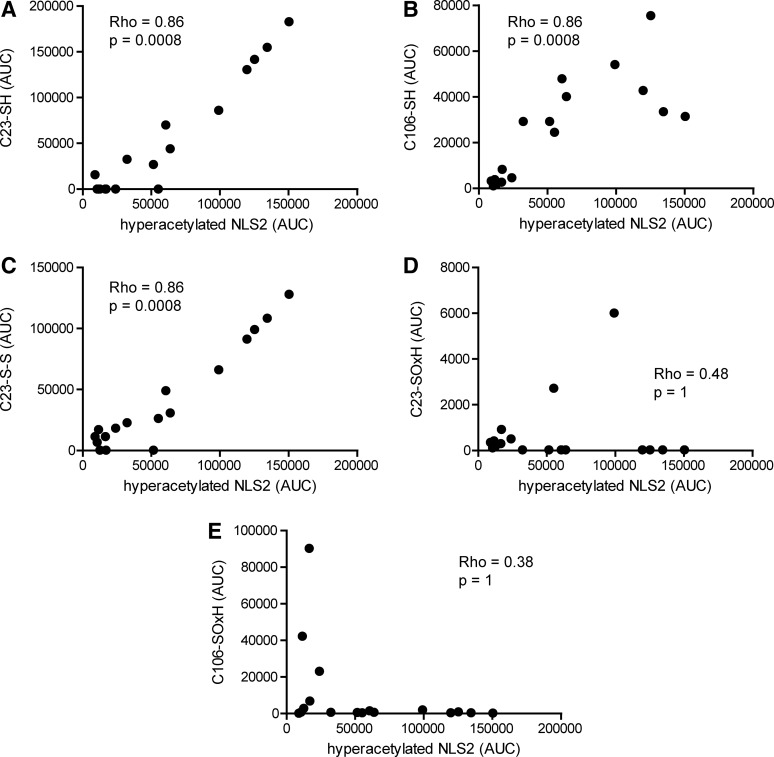
FIG. 8.
Actively released HMGB1 display different inflammatory functions. Cysteine modifications and acetylation of lysine residues were analyzed by LC-MS/MS, and peptide AUCs from LC-MS spectra were extracted. Iodoacetamide adducts are indicative of thiol cysteine side-chains (SH), whereas NEM adducts indicate participation in disulfide bond (S-S). (A) Correlation between extracted AUCs for C23 peptide with iodoacetamide adduct and hyperacetylated NLS2 peptide (B) Correlation between AUCs for C106 peptide with an iodoacetamide adduct and hyperacetylated NLS2 peptide (C) Correlation between extracted AUCs for C23 peptide with NEM adduct and hyperacetylated NLS2 peptide. (D) Correlation between combined extracted AUCs for oxidized C23 peptide modifications (C23-SOxH) and hyperacetylated NLS2 peptide. (E) Correlation between combined extracted AUCs for oxidized C106 peptide modifications (C106-SOxH) and hyperacetylated NLS2 peptide. Correlation coefficients and p-values were calculated using Spearman's rank correlation test and adjusted for multiple comparison (Holm's method). Sulfenic, sulfinic, and sulfonic cysteine side-chain modifications were collectively denoted as SOxH. Values below detection limit were substituted with the lowest limit of detection for that particular peptide modification. p-values<0.05 were considered significant.