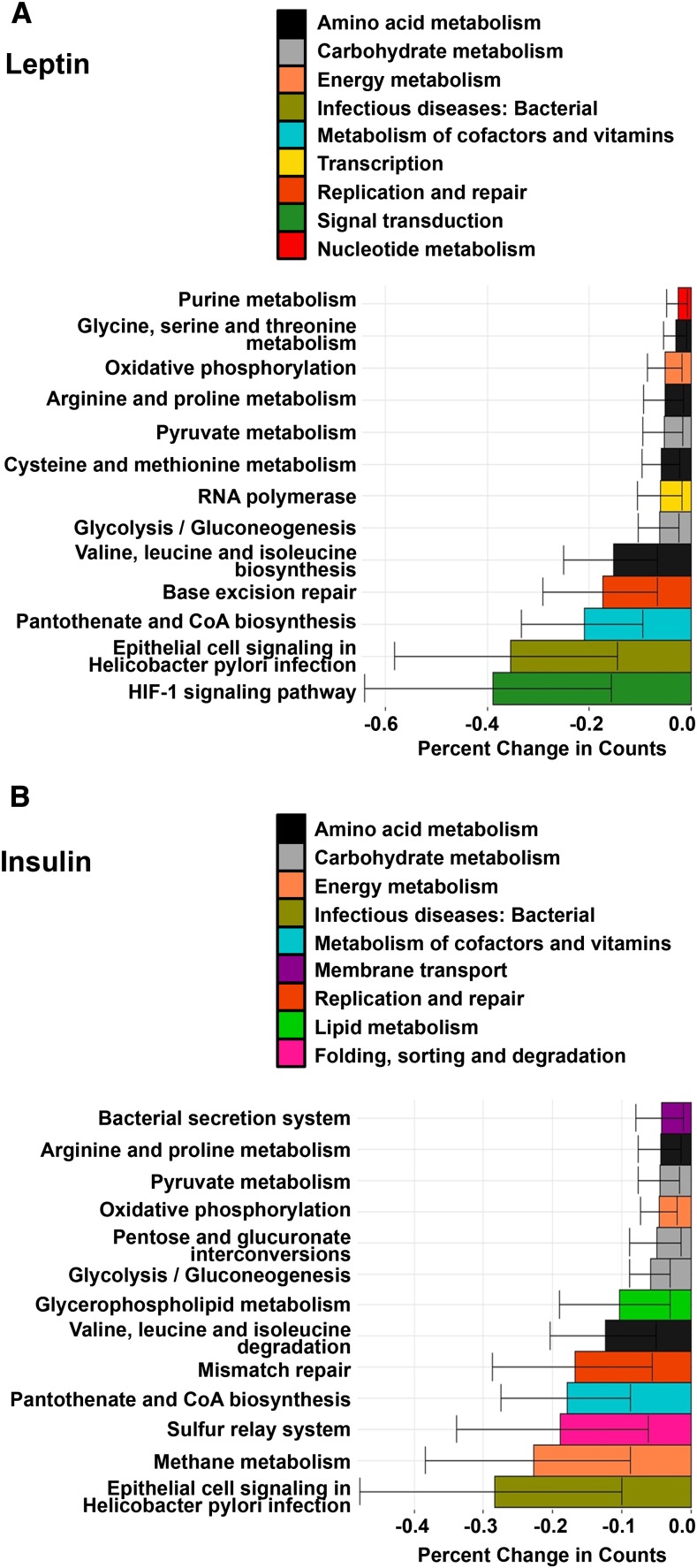
FIGURE 4.
HM leptin and insulin associated with changes in infant microbiome metagenome expression at the L2-level ontology. After adjustment for maternal BMI (n = 30), HM leptin (A) and insulin (B) were negatively associated with functional KO annotations from 2-wk infant microbiome composition representing pathways involved in bacterial amino acid, carbohydrate, vitamin, and energy metabolism, as well as with genes involved in cellular homeostasis and host intestinal barrier function. Outcomes presented are KO pathways from the L2 level with a total relative abundance ≥1% in all of the participants with the use of quasi-Poisson regression analysis (P < 0.01). Values are means ± SEs. HM, human milk; KO, KEGG Ortholog.