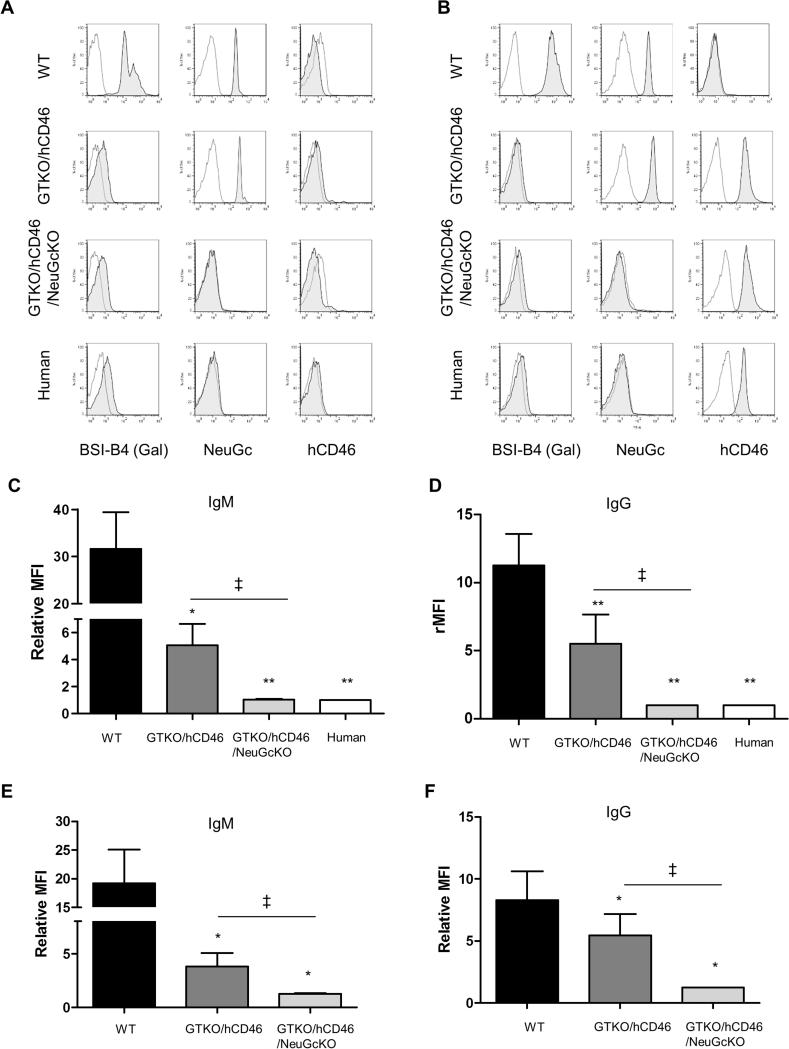
Figure 2.
Expression of Gal, NeuGc, and hCD46 on WT, GTKO/hCD46, and GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pig cells and on human cells - (A) RBCs, (B) PBMCs. Human IgM (C) and IgG (D) binding to WT, GTKO/hCD46, and GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pig and human RBCs. Human IgM (E) and IgG (F) binding to WT, GTKO/hCD46, and GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pig PBMCs. (To prevent a false positive result from alloantibody binding, human PBMC were not tested for IgM/IgG binding.) (A, B) Gal was detected only on WT RBCs and PBMCs. NeuGc was detected on RBCs and PBMCs from WT and GTKO/hCD46 pigs. RBCs and PBMCs from GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pigs and humans were negative for both Gal and NeuGc. The hCD46 molecule is not expressed on the surface of RBCs, but it is detected on the PBMCs from GTKO/hCD46 and GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pigs and from humans. (C, D) There was a significant difference in human IgM and IgG binding between WT vs. GTKO/hCD46, GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pRBCs, and human RBCs (*p<0.05, **p<0.01). There was also a significant difference in binding between GTKO/hCD46 and GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pRBCs (‡p<0.05). There was no IgM/IgG binding to GTKO/CD46/NeuGcKO pig and human RBCs (a relative MFI<1 indicates no significant binding of IgM or IgG). (E,F) There were significant differences in human IgM and IgG binding between WT and GTKO/hCD46 pPBMCs (*p<0.05) and GTKO/hCD46 and GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pPBMCs (‡p<0.05).