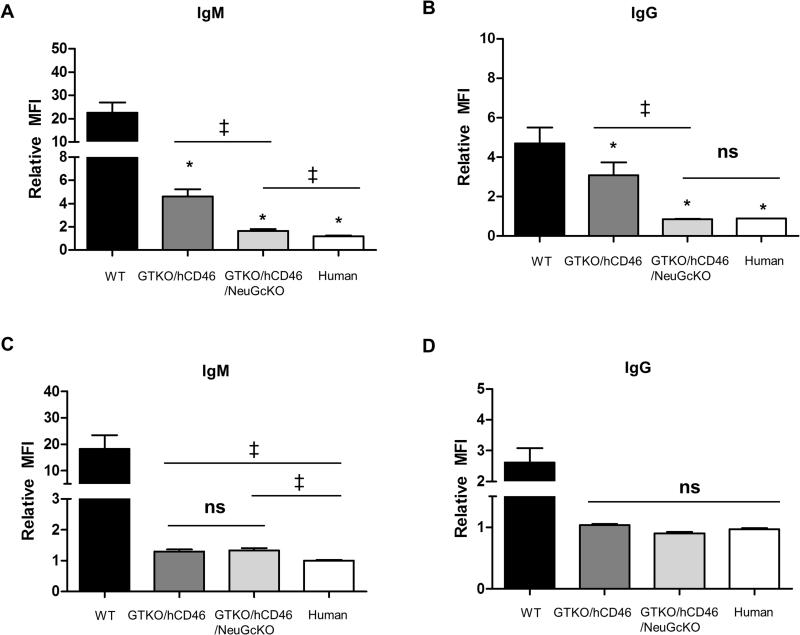
Figure 5.
Human IgM and IgG antibody binding to pig and human AECs (A, B) and CECs (C, D) by flow cytometry. (A, B) Human IgM and IgG binding to GTKO/hCD46 pAECs was significantly decreased compared to WT pAECs (*p<0.05), and was further decreased to GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pAECs (*p<0.05). Also, there was a significant difference in IgM and IgG binding to GTKO/hCD46 and GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pAECs (‡p<0.05). There was significantly greater IgM binding to GTKO/hCD46/NeuGcKO pAECs than human AECs (‡p<0.05), but there was no statistical significance in the extent of IgG binding between them. (C, D) Human IgM and IgG binding to WT pCECs was significantly greater than to CECs from the other pigs (*p<0.05), but there was no significant difference in binding between these other pigs.