Fig. 1.
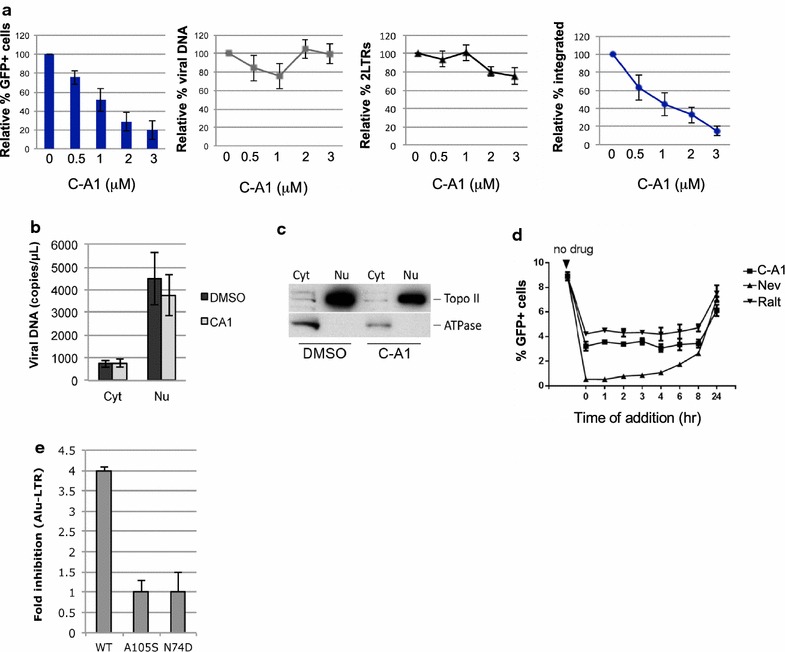
C-A1 inhibits HIV-1 integration and capsid mutations confer resistance to the drug. a Jurkat cells were infected with HIV-1GFP at an MOI of 0.05–0.1 in the presence of the indicated concentrations of C-A1 and analyzed by FACS 24 h later to determine the percentage of infected cells, the amount of viral DNA and 2LTR circular DNA. The amount of integrated viral DNA was determined by Alu-LTR TaqMan qPCR 10 days post-infection. b Jurkat cells were infected with HIV-1GFP at the same MOI in the presence or absence of 3 μM C-A1 and fractionated into a cytoplasmic and a nuclear fraction 16 h post-infection. The amount of viral DNA was measured by TaqMan qPCR in each fraction. c The quality of the fractionation was assessed by Western blot to detect DNA Topoisomerase II (Topo II) and Na/K ATPase (ATPase); representative of three experiments. d Time of addition assay. Jurkat cells were infected with HIV-1GFP at an MOI of 0.1 and the compounds were added at the indicated time points after infection (time 0). Cells were analyzed by FACS 36 h post-infection. e Jurkat cells were infected with HIV-1GFP WT, A105S or N74D capsid mutants at an MOI of 0.1 in the presence of 3 μM C-A1 and the quantity of integrated viral DNA was measured by Alu-LTR TaqMan qPCR 1 week post-infection. Average values ±SD of three independent experiments are shown in (a, b, e)
