Fig. 6.
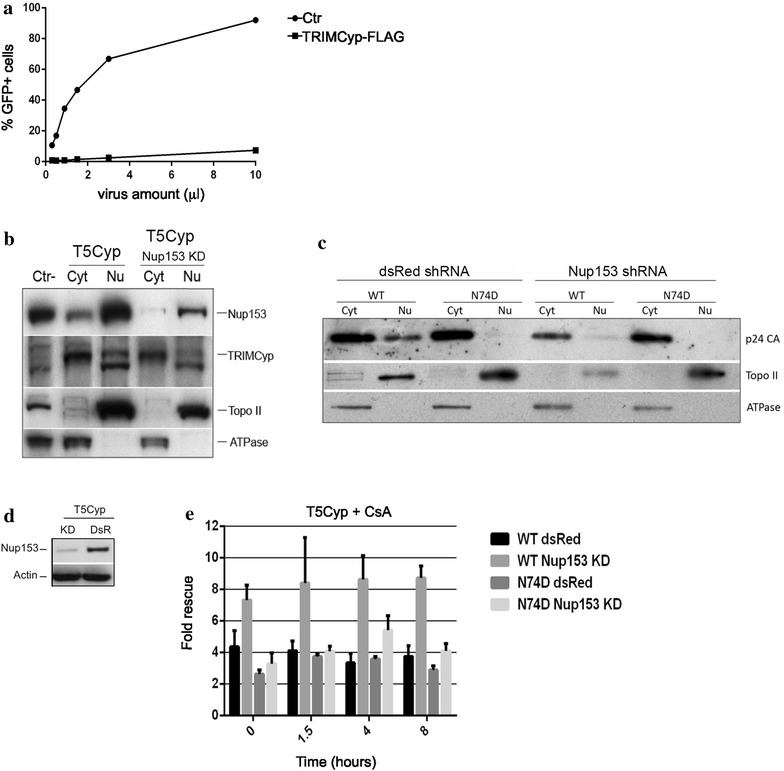
Depletion of Nup153 affects sensitivity to T5Cyp in CD4+ T cells. a Jurkat cells stably expressing a Flag-tagged TRIMCyp or an empty vector (Ctr) were infected with increasing doses of HIV-1GFP and analyzed by FACS 48 h later. b Cells stably expressing TRIMCyp were depleted of Nup153 using shRNA. Cells were fractionated into nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions and analyzed by Western blot to detect the distribution of TRIMCyp, Nup153, DNA Topo II and Na/K ATPase. Cyt cytoplasmic fraction, Nu nuclear fraction, Ctr-, Jurkat cells not expressing TRIMCyp. c Cells depleted of Nup153 or control cells expressing an shRNA targeting the Discosoma corallimorpharian mRNA (dsRed) were infected with HIV-1GFP at an MOI of 0.1 in the presence of CsA, fractionated into nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions and analyzed by Western blot to detect the distribution of capsid, DNA Topo II and Na/K ATPase. d Nup153 was depleted by shRNA in T5Cyp cells. An shRNA targeting DsRed (DsR) was used as control. e These cells were used to perform CsA washout assays upon infection with HIV-1GFP WT or capsid mutant N74D. Cells were analyzed by FACS 48 h post-infection and the fold rescue of infection induced by CsA was plotted. Depletion of Nup153 enhanced rescue of infection significantly in T5Cyp cells and the effect was specific for HIV-1GFP WT. Average values of rescue of infection ±SD are shown for three independent experiments
