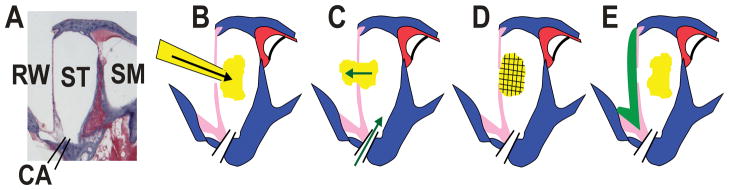
Figure 1.
Summary of injection, leaks and sealing procedures. A: Section of the basal turn of scala tympani from a guinea pig with fluid compartments labeled. Abbreviations are RW: round window; ST: scala tympani; SM: scala media; CA: cochlear aqueduct. B: Schematic showing injection through the RW membrane. The size of the injection pipette has been grossly exaggerated for clarity. C: Injected solution is displaced through the RW membrane perforation made by the injection pipette, driven by CSF entering through the cochlear aqueduct (green arrows). D: Internal sealing may be provided if the marker is injected as a viscous gel, which plugs the perforation site preventing fluid efflux. E: External sealing is achieved by applying adhesive (green) to the exterior surface of the RW membrane.