Figure 4.
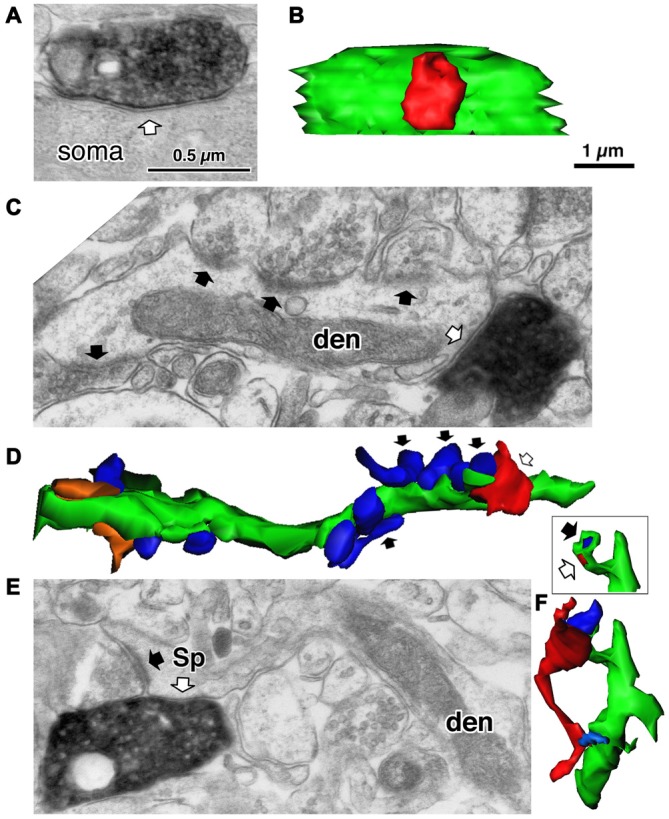
Three different target structures of the inhibitory synapses. (A) A symmetrical synapse (white arrow) of the LS neurogliaform (LS-NG) cell onto a postsynaptic soma. (B) 3D reconstructed image of the synaptic structure shown in (A). The axonal terminal of the LS NG cell (red) innervates the soma (green). (C) A symmetrical synapse (white arrow) from a corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) positive double bouquet cell onto a dendritic shaft (den) with frequent asymmetrical inputs (black arrows). (D) 3D reconstructed image (green) of the dendrite shown in (C). Arrows indicate the same axon terminal boutons shown in (C). Red is an axon terminal of the double bouquet cell. Blue structures are boutons forming asymmetrical synapses. Orange structures are boutons forming symmetrical synapses. (E) A symmetrical synapse (white arrow) from a CR positive double bouquet cell onto a spine head (Sp), which is also innervated by an asymmetrical synapse (black arrow). Scale in (A,C,E) shares the scale bar shown in (A). (F) 3D reconstructed image of synaptic structure shown in (E). An axon terminal of the double bouquet cell (red) innervates the spine head (green), which is also innervated by an asymmetrical synaptic terminal (blue). Inset shows the two synaptic junctions (red and dark blue) on the spine, without the presynaptic boutons. Scale in (B,D,F) share the scale bar shown in (B). Adapted from Kubota et al. (2007).
