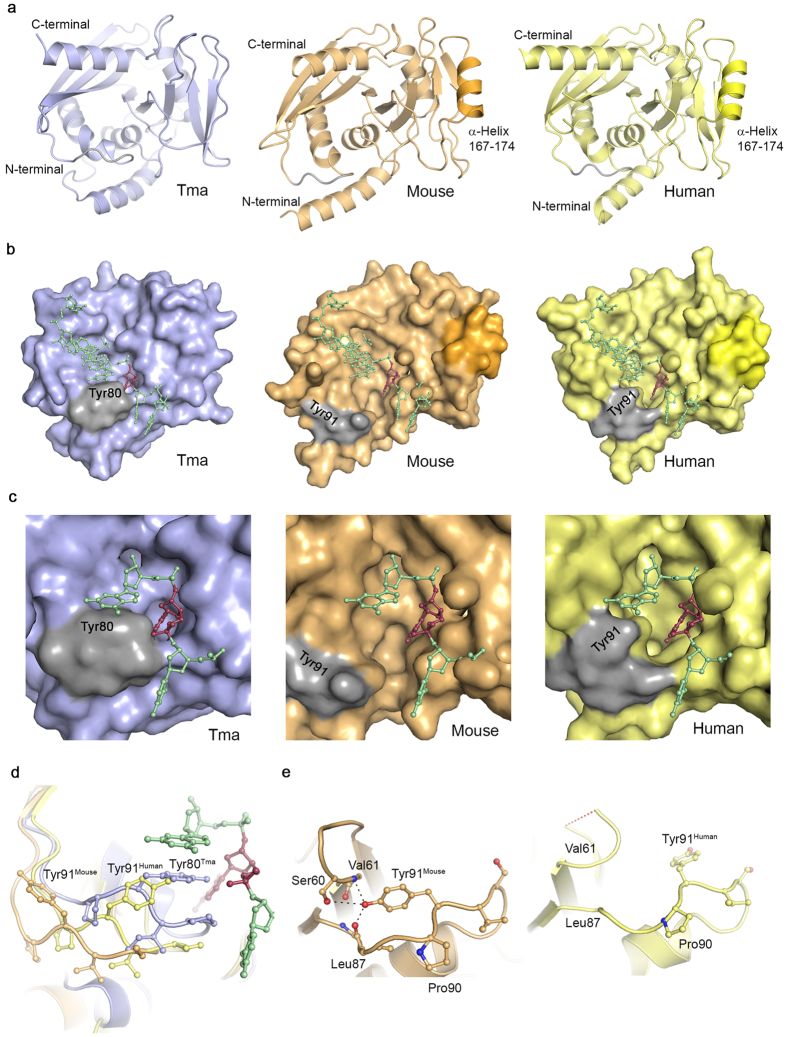
Figure 4. Endonuclease V structures.
(a) Overall structure of Thermotoga (blue), mouse (orange) and human (yellow) EndoV. The mammalian versions used in crystallization have been truncated (mouse 1–250, human 13–250). The additional α-helix common to the mammalian variants is colored in a stronger hue in mouse and human EndoV. (b) Surface display of Thermotoga, mouse and human EndoV. The wedge residues are colored gray; the surface contour of the mammal-specific helix is shown for mouse and human EndoV in a stronger hue. The lesion-strand in DNA in the complex with TmEndoV has been overlayed onto the mouse and human EndoV structures. The inosine residue is colored dark red. (c) Close-up view of the binding pocket regions of Thermotoga, mouse and human EndoV, illustrating the open character of mouse and human EndoV compared with the more closed TmEndoV. (d) The conformation of the wedge motif in Thermotoga (blue), mouse (orange) and human EndoV (yellow). The TmEndoV structure is that of the DNA bound form with the inosine lesion in dark red. (e) Close-up view of the Tyr91 conformation in mouse and human EndoV. The hydrogen bond between mouse Tyr91, Ser60, Val61 and Leu87 are shown (left) and compared with the similar open region in hEndoV (right). The red dashed line in the loop in hEndoV indicates disordered residues not present in the structural model.