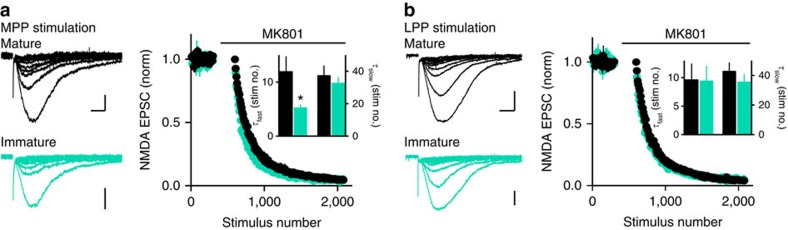
Figure 5. Release probability at mature and immature synapses.
(a, left) Examples of progressive block of MPP-evoked NMDA EPSCs in mature (black) and immature GCs (teal). Every 10th EPSC is shown. Scale bars, 50 pA, 20 ms. (right) The normalized amplitude of NMDA EPSCs is plotted against stimulus number and fit by two exponentials. The fast component (τfast) was faster in immature GCs (τfast: 5.2±0.6, n=8, compared with 11.9±2.8, n=8, P=0.037, unpaired t-test), suggestive of higher release probability. Grouped data include both simultaneous recordings from mature and immature GCs (n=5 cell pairs) and individual GC recordings (n=3 cells, total of n=8). (b, left) Examples of MK801 block of LPP-evoked NMDA EPSCs. Scale bar: 100 pA (top), 20 ms; or 50 pA (bottom), 20 ms. The blocking rate was the same in mature and immature GCs (n=8 each, P=0.98).