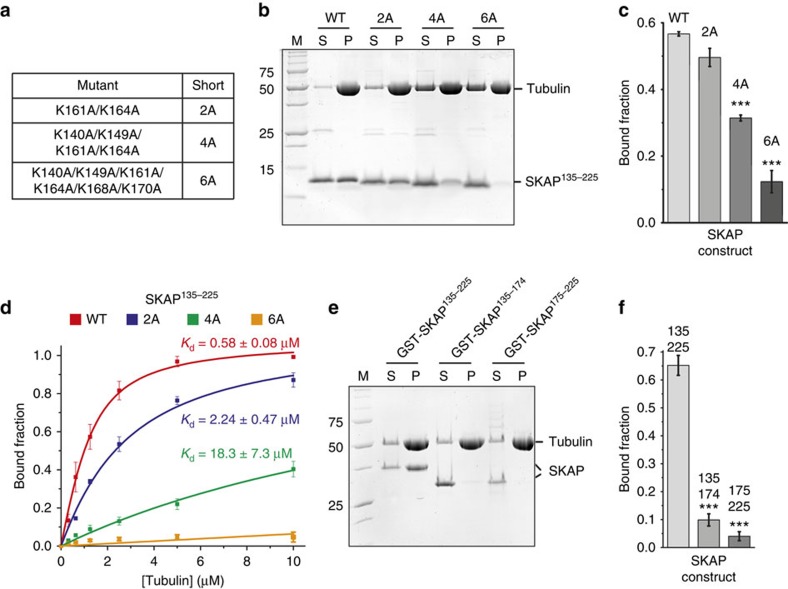
Figure 3. Multiple positively charged residues are required for microtubule binding of SKAP in vitro.
(a) Summary of alanine point mutants created based on cross-linking analysis. (b) Representative SDS–PAGE of microtubule co-sedimentation assays with 3 μM taxol-stabilized microtubules and 3 μM SKAP135–225 wild type (WT) or indicated mutants. M, molecular weight marker; P, pellet fraction; S, soluble fraction. (c) Quantification of microtubule co-sedimentation assays shown in b (mean±s.e.m., n=3, t-test: ***P<0.001). (d) Quantification and fitting analysis of microtubule co-sedimentation assays with 0–10 μM taxol-stabilized microtubules and 1 μM SKAP135–225 WT or indicated mutants (mean±s.e.m., n=3). (e) Representative SDS–PAGE of microtubule co-sedimentation assays with 3 μM taxol-stabilized microtubules and 3 μM GST-SKAP135–225, GST-SKAP135–174 or GST-SKAP175–225. M, molecular weight marker; P, pellet fraction; S, soluble fraction. (f) Quantification of microtubule co-sedimentation assays shown in e (mean±s.e.m., n=3, t-test: ***P<0.001).