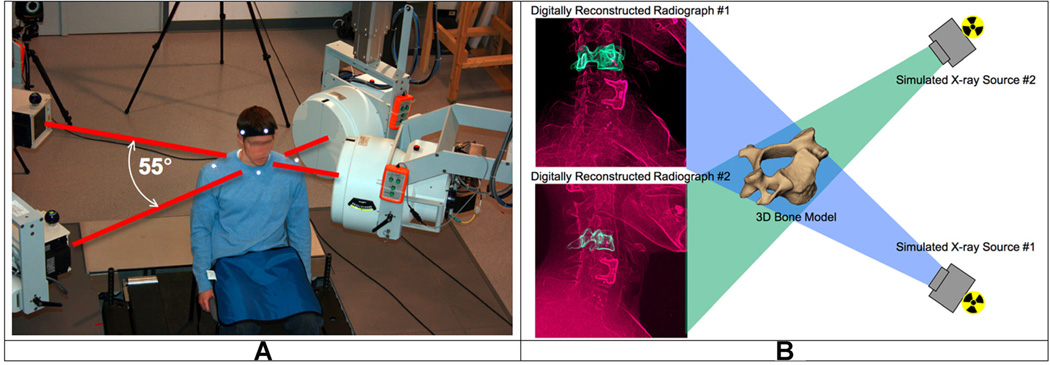
Figure 1.
The biplane radiography system and bone-model-based tracking technique. (A) The biplane radiography system was configured with an angle of approximately 55° between X-ray tube/image intensifier pairs. Each cardiac cine-angiography generator produced short duration (2.5 ms), high powered (70 kVp, 160 mA), X-ray pulses at a rate of 30 pulses per second. (B) The virtual X-ray system for model based tracking. A 3D CT reconstruction of the bone was placed in a computer-generated reproduction of the X-ray system. Simulated X-rays were then passed through the 3D CT reconstruction to generate digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs). Bone position and orientation was determined by a computer algorithm that optimized the correlation between the DRRs (green in image) and the edge-enhanced radiographs (red in figure).