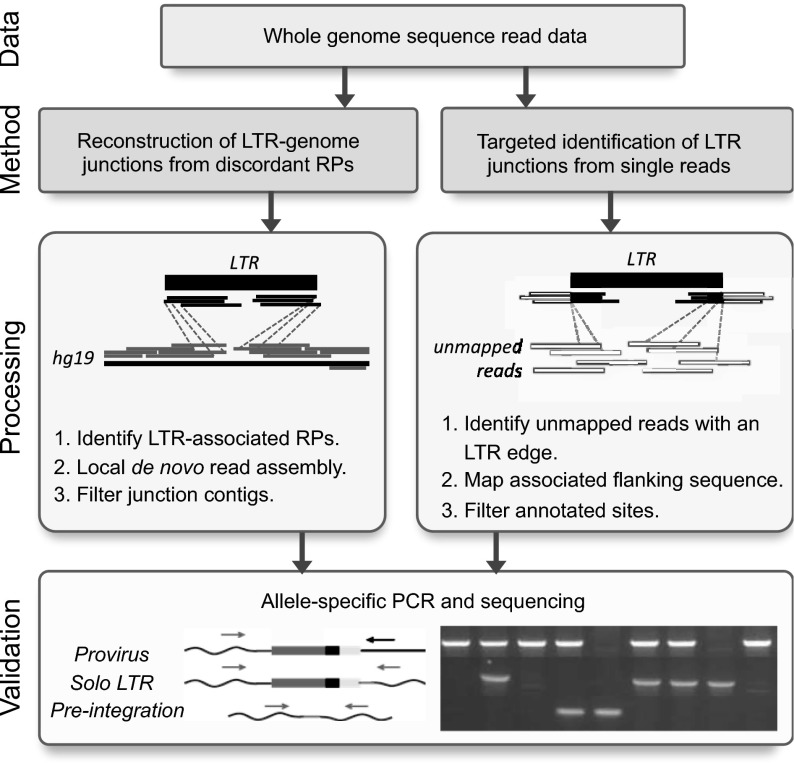
Fig. 1.
Approaches for the detection of nonreference HML-2 insertions from WGS read data. Illumina short reads were processed by one of two methods. (Left) Read pairs (RPs) were identified that have one read mapped to the genome (gray) and mate to reads that map to the sequence matching the HML-2 LTR consensus (black). Supporting reads from each site were extracted and subjected to local assembly, and the resulting contigs were analyzed for the presence of LTR–genome junctions. (Right) Unmapped reads from each sample were identified that contained a sequence corresponding to the LTR edge, and the cognate sequence was then used to determine candidate integration positions from genomic data. (Bottom) PCR and capillary sequencing were used to validate candidate insertions in reactions that used flanking primers (gray arrows) to detect the presence of a solo-LTR or empty site, or a flanking primer paired with an internal proviral primer (black arrow) to infer the presence of a full-length allele. Representative products are shown in a genotyping gel to the right.