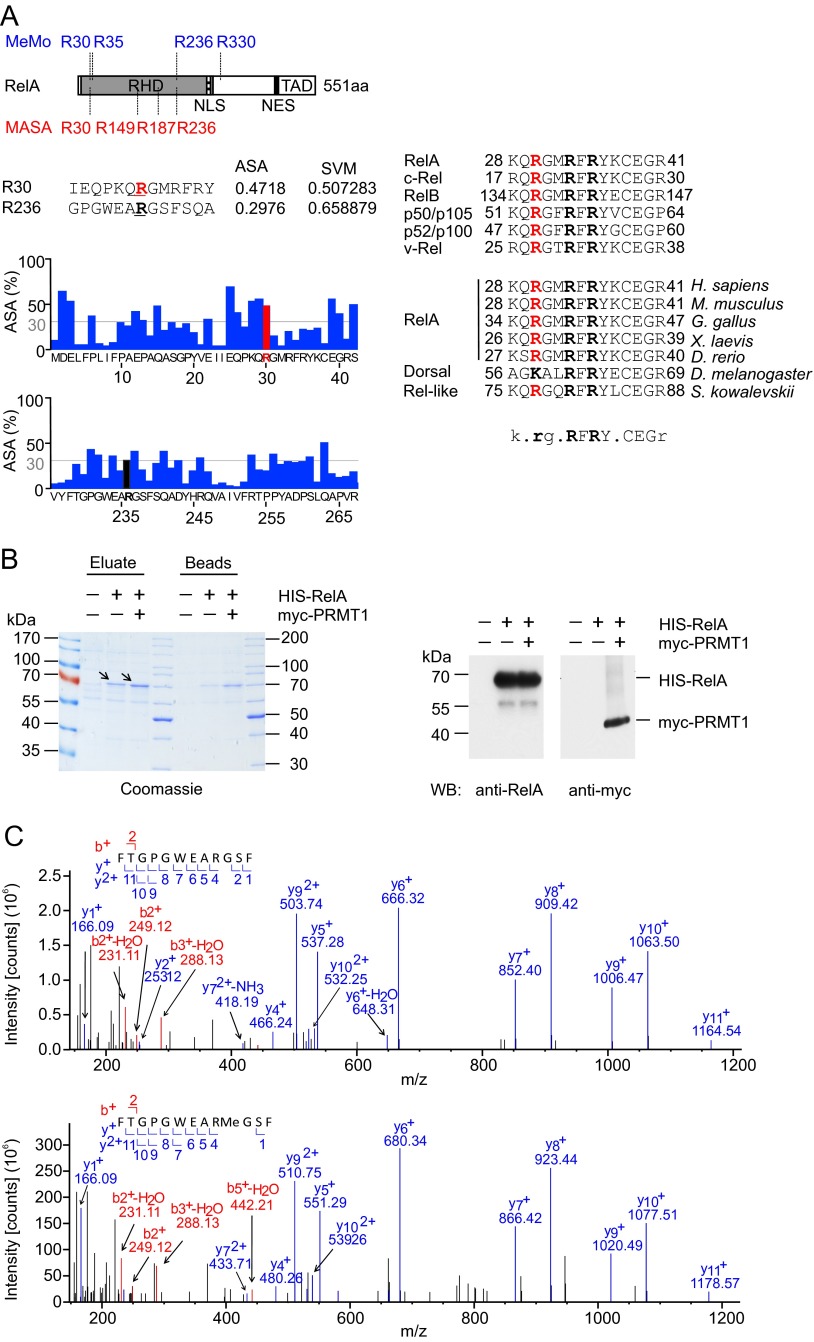
Fig. S1.
Identification of methylation sites in RelA. (A) In silico analysis of putative methylation sites in RelA by MeMo 2.0 and MASA 1.0. (Left) Schematic representation of the RelA protein as described in Fig. 1B. (Upper) Positions of predicted methylation sites. (Lower) Analysis of solvent-accessible surface areas surrounding R30 and R236 residues performed using MASA 1.0. (Right) Alignment of protein sequences adjacent to R30 among different species and NF-κB family members. (B) His-RelA (arrows) was purified from control, His-RelA–expressing, or His-RelA and myc-PRMT1–expressing HEK 293T cells using Ni-NTA beads. Proteins were eluted from beads with 0.1% TFA/50% (vol/vol) acetonitrile, and pH was neutralized by adding triethylammonium bicarbonate (TEAB) buffer. A 1/6th part of the eluate was analyzed by SDS/PAGE (Left), and a 1/20th part was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-RelA(C20) antibodies (Right). The expression of myc-PRMT1 was confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-myc 9E10 antibody. (C) MS/MS spectra of the nonmethylated (Upper) and monomethylated (Lower) peptide 228FTGPGWEARGSF239 containing R236.