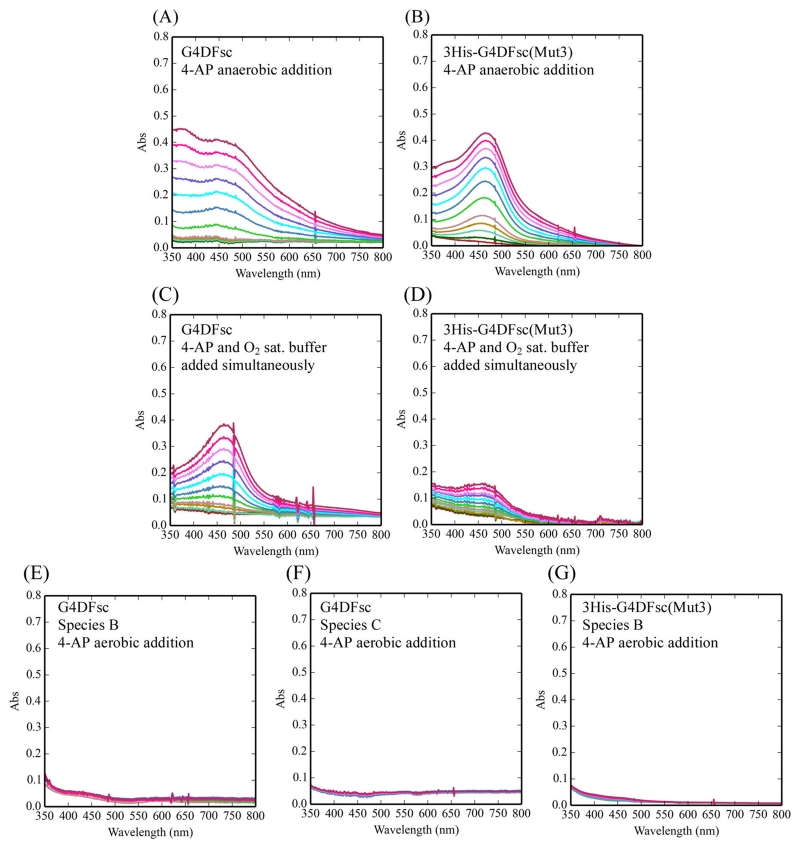
Figure 3.
Oxidation of 4-aminophenol (4-AP) for various reaction conditions over 10 min. The reaction conditions include the following: (1) the addition of O2-saturated buffer to biferrous G4DFsc (A) and 3His-G4DFsc(Mut3) (B) with 4-AP (in the presence of m-phenylenediamine) already loaded; (2) the simultaneous addition of O2-saturated buffer and 4-AP (in the presence of m-phenylenediamine) to biferrous G4DFsc (C) and 3His-G4DFsc(Mut3) (D); and (3) the addition of 4-AP (in the presence of m-phenylenediamine) to the biferric paramagnetic Species B (E) and diamagnetic Species C (F) for G4DFsc and the biferric diamagnetic Species B for 3His-G4DFsc(Mut3) (G). Aminoindoaniline dye formation was used to identify the oxidation of 4-AP (see Figure 2). Final concentrations (after O2-saturated buffer addition) were 10 μM protein, 3.9 mM 4-AP, and 10 mM m-phenylenediamine.