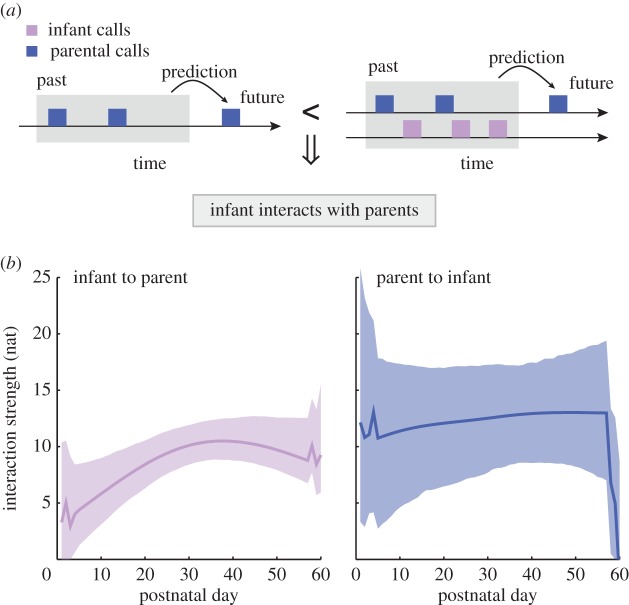
Figure 3.
Granger causality quantifies interactions between infants and parents. (a) Illustration of the idea of Granger causality. An interaction from infant to parent vocalization exists if the prediction using only past parental vocalizations is worse than the prediction using the past parental and infant vocalizations. (b) Average interaction strength from infant to parent (purple line) and from parent to infant (blue line). Larger values indicate stronger interactions. Dashed regions indicate the respective 95% confidence intervals.