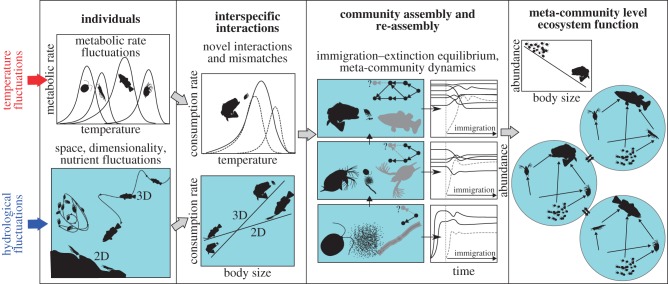
Figure 1.
A conceptual framework for studying the effects of environmental fluctuations on running water ecosystems. ‘2D’ and ‘3D’ refer to two and three spatial dimensions, respectively. Both, temperature and hydrological fluctuations affect individuals, which are then propagated through species interactions to higher levels of organization. Species interactions are likely to be disrupted also due to inter-specific mismatches arising from the differing tolerances, physiologies or biomechanics of predator and prey. Note also that ectotherm thermal performance curves are typically asymmetric (as shown)—i.e. heat waves are likely to have far stronger impacts than cold spells on species and interactions.