Table 1.
Reaction optimization: Lewis Acid and chiral diol screen.[a]
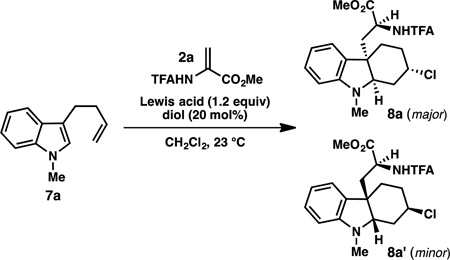 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Lewis Acid |
Diol | Yield 8 (%)[b] |
dr | ee 8a (%)[c] |
| 1 | SnCl4 | (R)-BINOL (L1) | 19 | 10:1 | 88 |
| 2 | TiCl4 | (R)-BINOL | 27 | 6:1 | 0 |
| 3 | SbCl5 | (R)-BINOL | 0 | -- | -- |
| 4 | ZrCl4 | (R)-BINOL | 30 | 9:1 | 40 |
| 5 | Zr(OtBu)4 | (R)-BINOL | 0 | -- | -- |
| 6 | ZrCl4 | (R)-6,6’-dibromo-BINOL (L2) | 38 | 9:1 | 30 |
| 7 | ZrCl4 | (R)-3,3’-dibromo-BINOL (L3) | 40 | 7:1 | 76 |
| 8 | ZrCl4 | (S)-VANOL (L4) | 33 | 6:1 | 74 |
| 9 | ZrCl4 | (4R, 5R)-Ph-TADDOL (L5) | 37 | >10:1 | 66 |
Reactions conducted with 0.20 mmol 7a and 0.24 mmol 2a.
Combined isolated yield of two diastereomers.
The ee of the major diastereomer was determined by SFC using a chiral stationary phase.
