Figure 1.
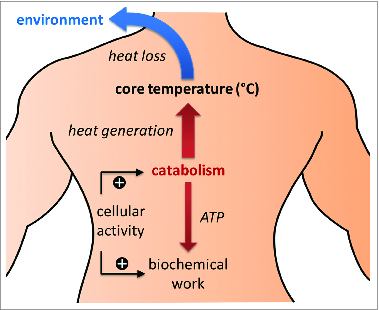
Determinants of core temperature and general approaches to its modulation. Core temperature is determined by the balance of heat generation through catabolism and heat loss to the environment (assuming most typical conditions, in which ambient temperature is lower than core temperature). Catabolism is a component of the cellular activity that provides energy for other biochemical processes. Increased cellular activity results in increased rates of catabolism and heat generation. Heat loss depends on the gradient between ambient and core temperatures. Core temperature may be lowered by decreasing heat generation through the reduction of cellular activity, and/or by increasing heat loss through the lowering of ambient temperature (i.e., application of physical cooling).
