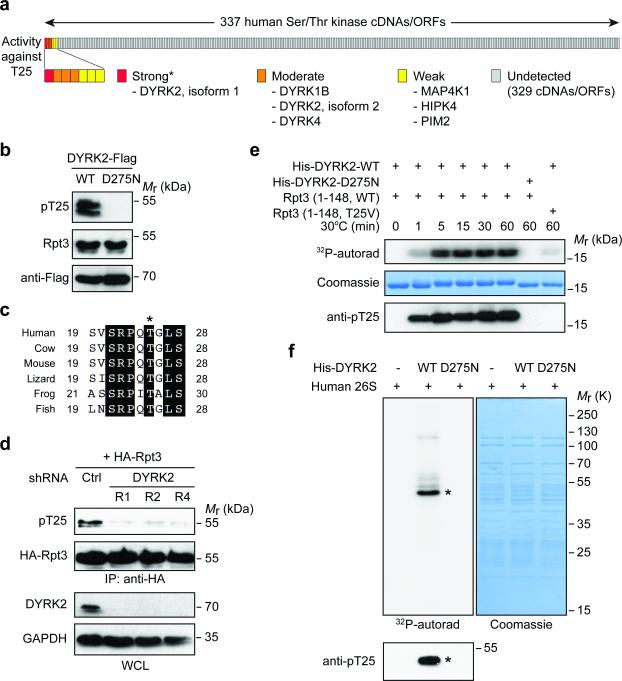
Figure 4. DYRK2 is the primary Rpt3-T25 kinase.
(a) Summary of the Rpt3-T25 kinase screen. Each vertical bar represents an individual kinase cDNA/open reading frame (ORF). The activity of each kinase towards endogenous Rpt3-T25 in 293T cells is marked as strong (red), moderate (orange), weak (yellow) or undetected (gray). *DYRK3 cDNA from the kinase library failed to express properly, although the kinase could strongly phosphorylate T25 when overexpressed (see Supplementary Fig. 4a).
(b) 293T cells were transfected with WT DYRK2 or the catalytically inactive mutant, D275N. T25 phosphorylation of endogenous Rpt3 is blotted from whole cell lysates.
(c) An alignment of vertebrate Rpt3 protein sequences surrounding Thr25 (asterisk). The sequences shown are NP_006494 (human), NP_001030255 (cow), NP_036004 (mouse), XP_008119139 (lizard), NP_001008010 (frog) and NP_956044 (fish).
(d) DYRK2 knockdown decreases T25 phosphorylation. HA-Rpt3 (WT) was transfected into 293T cells stably expressing control or three independent DYRK2 shRNAs. Following anti-HA IP, T25 phosphorylation was determined by western blot.
(e) Time-dependent phosphorylation of recombinant human Rpt3 (aa 1-148) by bacterially expressed DYRK2 (aa 74-479), indicated by 32P-phosphate incorporation (top), gel shift (middle) and anti-pT25 western blot (bottom).
(f) In vitro kinase assay with DYRK2 and purified human 26S proteasome. Asterisk indicates the most strongly phosphorylated band, which matched with the anti-pT25 blot (bottom).