Figure 1.
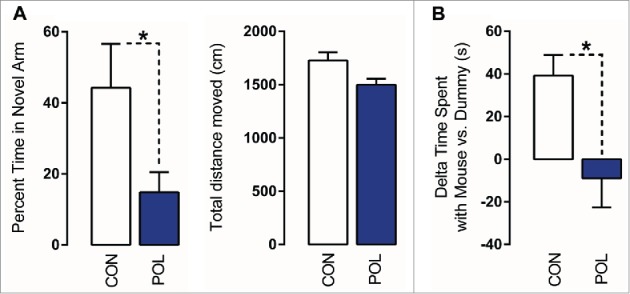
Prenatal immune activation produces working memory and social interaction deficits. (A) Working memory was assessed in the Y-maze spatial recognition paradigm. Left: The bar plot depicts the percent time spent in the novel (previously unexplored) arm during the choice phase of the test in control (CON) and poly(I:C) (POL) offspring. *P < 0.05 as determined by a Student t-test. Right: The bars plot shows the total distance moved during the choice phase of the test. (B) Social interaction was assessed by analyzing the relative exploration time between an unfamiliar congenic mouse (‘mouse’) and an inanimate dummy object (‘dummy’). The bar plots show the relative exploration time between the mouse and the dummy for the CON and POL offspring. *P < 0.05 as determined by a Student t-test. N(CON) = 8, N(POL) = 8. All values are means ± SEM.
