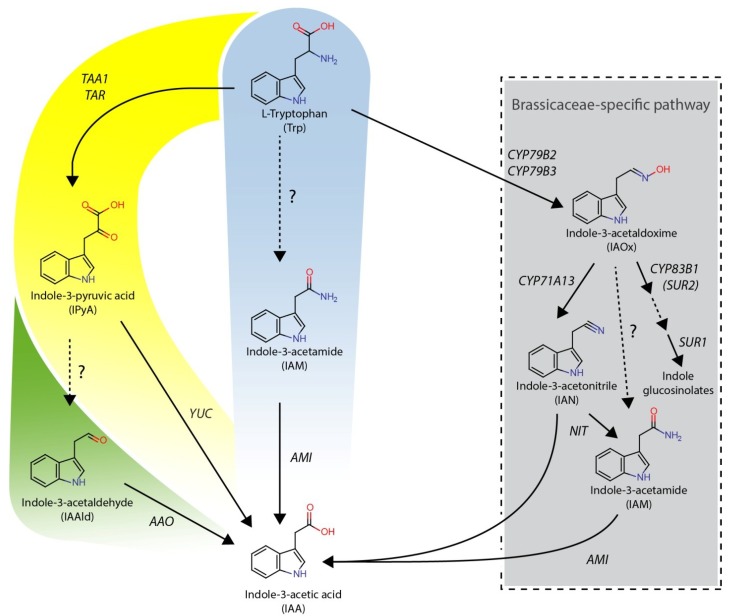
Figure 1.
Proposed pathways of L-tryptophan-dependent IAA biosynthesis in plants. The IAOx-pathway that is seemingly restricted to indole glucosinolate-producing plant species is given in the grey box. In yellow, the IPyA-pathway is shown; a possible side-branch (IAAld-pathway) is added in green to the IPyA-pathway. In the middle, the IAM-pathway is highlighted in blue. Dashed lines indicate assumed reaction steps for which the corresponding enzymes have yet to be identified.
Enzymes are abbreviated as follows: AAO, ARABIDOPSIS ALDEHYDE OXIDASE 1; AMI, AMIDASE; CYP71A13, CYTOCHROME P450 MONOOXYGENASE 71A13; CYP79B2/B3, CYTOCHROME P450 MONOOXYGENASE 79B2/B3; CYP83B1, CYTOCHROME P450 MONOOXYGENASE 83B1; NIT, NITRILASE; SUR1, SUPERROOT 1 (S-ALKYL-THIOHYDROXIMATE LYASE); TAA1, TRYPTOPHAN AMINOTRANSFERASE OF ARABIDOPSIS 1; TAR2, TRYPTOPHAN AMINOTRANSFERASE RELATED 2; YUC, YUCCA.