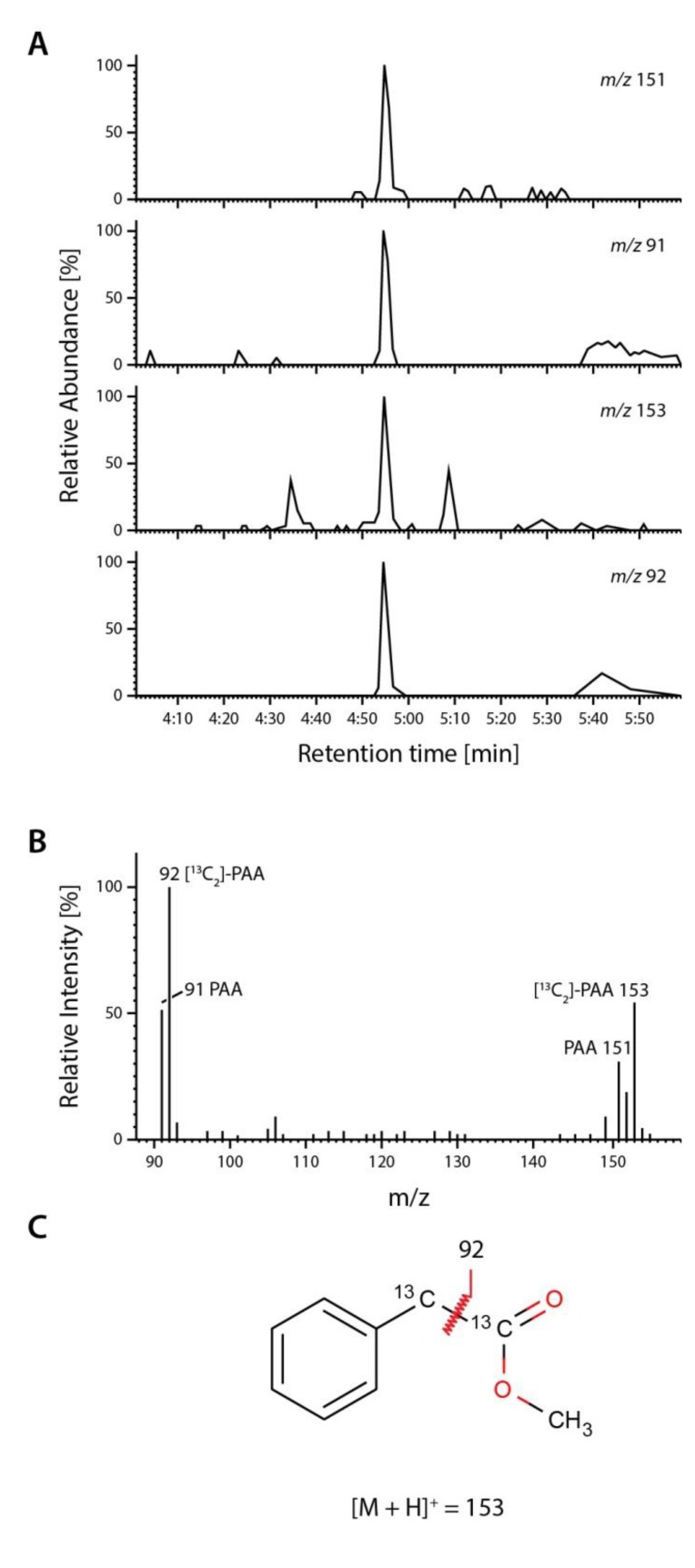
Figure 7.
Detection of endogenous PAA. Endogenous PAA in sterile-grown A. thaliana was analyzed by extracting the organic compounds from rosettes of two-week old plants with boiling methanol in the presence of 1 nmol [13C2]-PAA standard (Sigma). (A) The extract was pre-purified by solid-phase extraction and analyzed by GC-MS. Under these conditions, PAA elutes at 4:55 min. The upper panel shows the extracted ion chromatograms for endogenous PAA (m/z 91 and 151) and stable isotope labeled [13C2]-PAA (m/z 92 and 153); (B) The middle panel shows the characteristic full-scan mass spectrum for co-chromatographed endogenous PAA (m/z = 91, 151) and [13C2]-PAA (m/z = 92, 153); (C) Fragmentation and structure of the [13C2]-PAA methyl ester. As the two 13C atoms in [13C2]-PAA are attached to the acetate side chain, which is cleaved during ionization, only the mass of the parent ion of the labelled standard shows a shift of +2 atomic mass units relative to the endogenous compound. In consequence of fragmentation, however, the mass of the fragment of the standard PAA is shifted by only +1 atomic mass unit.