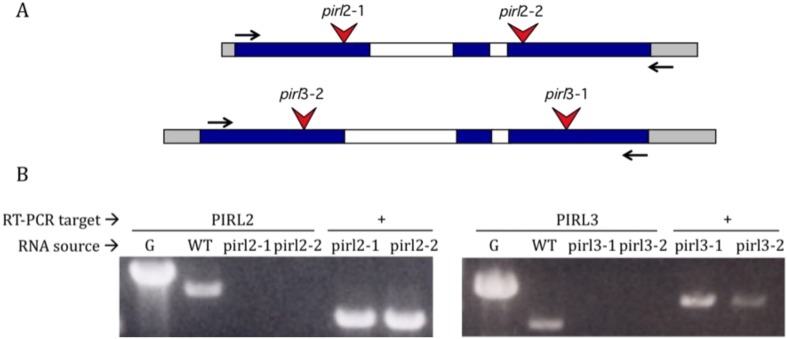
Figure 2.
PIRL2 and PIRL3 T-DNA insertion alleles and knockout status. (A) PIRL2 and PIRL3 gene maps, with exons shaded and introns shown in white; light gray shading indicates UTR regions. Positions of T-DNA insertions in pirl2-1, pirl2-2, pirl3-1, pirl3-2 alleles are indicated by red arrows. Horizontal arrows indicate positions of RT-PCR primers used for part B; (B) Confirmation of knockout status in pirl2 and pirl3 DNA insertion lines. RT-PCR was carried out with gene-specific primers on total RNA isolated from flowers or leaves of homozygous mutant (pirl2-1, pirl2-2, pirl3-1, or pirl3-2, as indicated) or wild-type (WT) controls. G, PIRL gene (with introns) amplified from genomic DNA.(+) lanes contain RT-PCR products for PIRL9 or PIRL1 amplified from pirl2 or pirl3 mutants, respectively, as positive controls for RNA quality and RT-PCR efficacy.