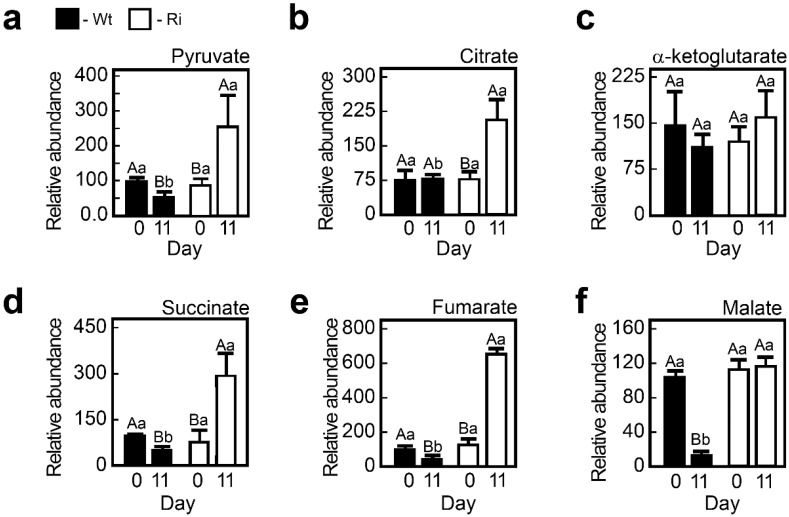
Figure 3.
The levels of pyruvate, the product of glycolysis, and tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) cycle intermediates in wild-type (Wt) and SO RNA interference mutants (Ri) plants grown under normal growth conditions (0, day) and after being exposed to eleven days of extended dark stress (11, day). Top leaves of Wt and Ri tomato plants were used to determine pyruvate (a); citrate (b); a-ketoglutarate (c); succinate (d); fumarate (e) and malate (f) content. The bars are the average values ± SE (n = 3–8). The values denoted with different letters are significantly different according to the Turkey-Kramer HSD test (JMP 8.0 software, [37]; p < 0.05). Different lower case letters indicate differences between the SO mutants and wild-type plants within the same treatment. Different upper case letters indicate significant difference within the plant genotypes in response to treatment. The data for SO-compromised plants represent the mean for SO Ri 131 and SO Ri 421 mutants.