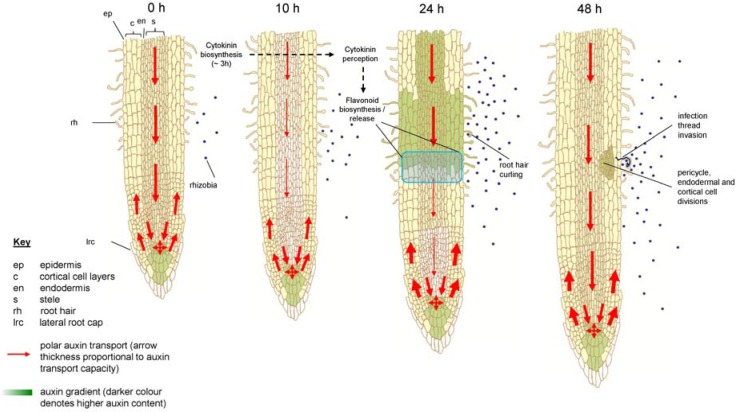
Figure 3.
Schematic model of the regulation of auxin transport during nodulation in Medicago truncatula. Before rhizobia infection, auxin (indole-3-acetic acid) is transported in the acropetal direction towards the root tip. Auxin is also transported in the basipetal direction (from root tip to elongation zone) in the outer layer(s). Within 3 h after symbiosis induction (lipochitooligosaccharide treatment), cytokinin biosynthesis is upregulated in M. truncatula roots [215]. Cytokinin perception at the inner cortex induces/releases certain flavonoids, which act as inhibitors of acropetal auxin transport at the inner cortical, endodermal and/or pericycle directly underlying the rhizobia infection site [212]. Acropetal auxin transport inhibition has been observed as early as 10 h after rhizobia infection [195]. The reduction of acropetal auxin transport increases auxin concentration at the rhizobia infection site, the location of a future nodule primordium. An increase in basipetal auxin transport could also contribute to the increased auxin pool at the nodulation site [212]. Pericycle, endodermal and cortical cell divisions are activated within 48 h.