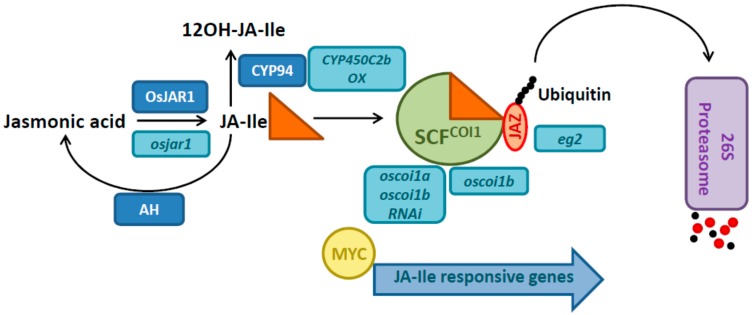
Figure 2.
Activation, inactivation, perception and signaling of JA. Names of mutants and transgenic lines are shown in light blue boxes. JAR1 catalyzes the conjugation of JA to isoleucine (JA-Ile). Several alleles of rice jar1 mutants are available because it is a hotspot of Tos17 retrotransposon insertion. Further GH3 enzymes may contribute to the biosynthesis of JA-Ile in rice. JA-Ile is recognized by its receptor COI1, which functions as E3 ubiquitin ligase in a SCF complex. Subsequently, JAZ proteins are recognized by the hormone receptor complex, poly-ubiquitinated and degraded in the 26S proteasome. Extra glume 2 (eg2) is a mutant of OsJAZ1. MYC transcription factors are released from repression by JAZ proteins and can activate transcription of early response genes. JA-Ile can be inactivated by CYP94 enzymes or amidohydrolases. In transgenic approaches, signaling has been affected by overexpressing CYP84C2b. Abbreviations: JA-Ile: jasmonoyl-isoleucine, JAR1: JASMONATE RESISTANT 1, COI1: CORONATINE INSENSITIVE 1, JAZ: JASMONATE ZIM-domain, CYP94: CYTOCHROME P450 CYP94 subfamily, AH: AMIDOHYDROLASES.