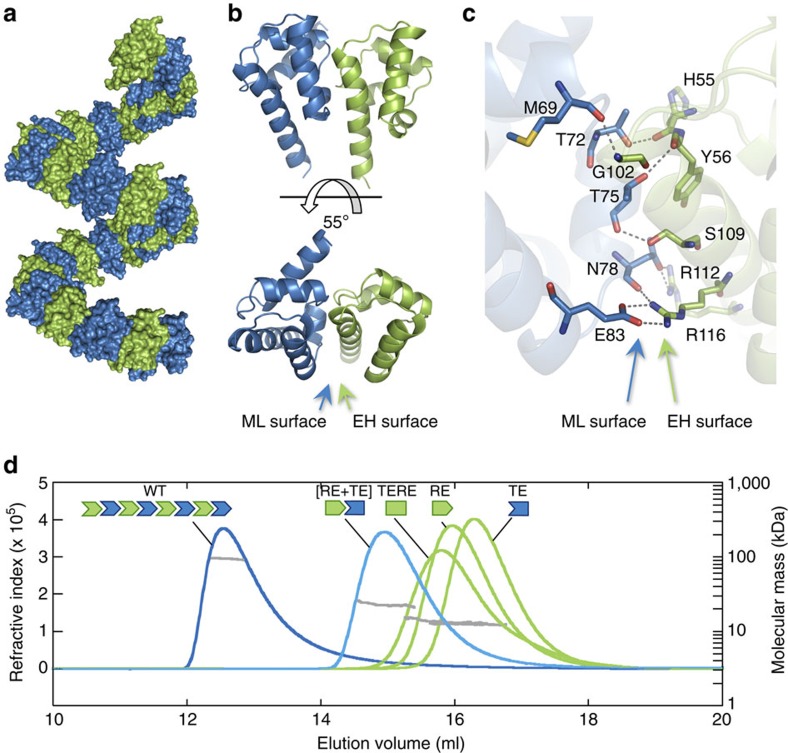
Figure 2. LFY-SAM is an oligomerization domain.
(a) Helical polymer of GbLFY-SAM in the crystal structure. Twenty-eight monomers are shown, alternatively coloured in blue and green. (b) Side and top views (upper and bottom panels, respectively) of the GbLFY-SAM dimer in the asymmetric unit of the crystal. ML and EH interaction surfaces are indicated. (c) Detailed view of GbLFY-SAM oligomerization interface. Residues mediating contacts between the two monomers are shown as sticks; residues on the ML and EH surfaces are in blue and green, respectively. (d) SEC-MALLS analysis of GbLFY-SAM (WT), GbLFY-SAMTE (TE, T75E substitution at the ML surface) and GbLFY-SAMRE (RE, R112E substitution at the EH surface), GbLFY-SAMTERE (TERE, T75E, R112E) double mutant and GbLFY-SAM[RE+TE] ([RE+TE], an equimolar mixture of GbLFY-SAMTE and GbLFY-SAMRE). 50 μl at ∼4.5 mg ml−1 of proteins were used. Elution profiles were monitored by excess refractive index (left ordinate axis). The grey line under each elution peak shows the molecular mass distribution (right ordinate axis). Measured molecular masses (reported in Supplementary Table 1) show that GbLFY-SAM is oligomeric; GbLFY-SAMTE, GbLFY-SAMRE and GbLFY-SAMTERE are monomeric; and GbLFY-SAM[RE+TE] is dimeric.