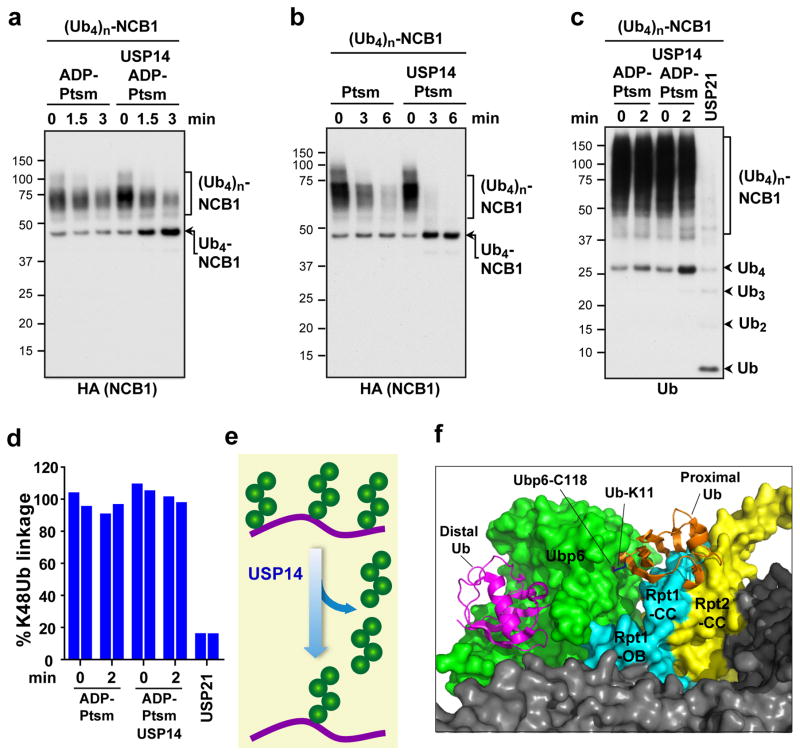
Figure 2. USP14 cleaves arrayed tetraubiquitin chains proximally, stopping at the last chain.
a, K48-linked Ub4 conjugates of NCB1 were prepared, resulting in one or more tetraubiquitin modifications. ADP-Ptsm (3 nM) was incubated with multi-K48Ub4-NCB1 (~90 nM) in the presence or absence of USP14 (60 nM). Arrow indicates K48Ub4-NCB1 species modified with a single chain and derived by USP14 cleavage. b, Assays as in a, except in the presence of ATP. c, K48Ub4-multichain conjugate of NCB1 was purified, and assays were performed as in a, except that a control was added in which the pan-specific deubiquitinating enzyme USP21 (0.5 μM) was used (10 min incubation). Arrowheads indicate free Ub4 chains released by USP14 (K48Ub4) and products of USP21 activity such as free Ub. Samples were analysed by SDS–PAGE/immunoblotting for HA (a and b) or Ub (c). d, Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) labeling and quantitative mass spectrometry. Purified K48Ub4-multi-chain NCB1 conjugates were assayed in biological duplicates for each condition as in a. The reaction was then quenched and subjected to trypsin digestion, TMT labeling, and tMS2 analysis in a Q-Exactive for quantification of K48-linked Ub peptides. e, Proposed en bloc mode of deubiquitination by USP14. f, Modeling of free ubiquitin chain cleavage by proteasome-activated Ubp6. Access of a K11-linked di-ubiquitin chain to the active site of Ubp6 appears occluded. Structures were obtained from the PDB database: Ubp6 and proteasome (5A5B)5 and Ub (1UBQ). C118 contains the active site nucleophile.