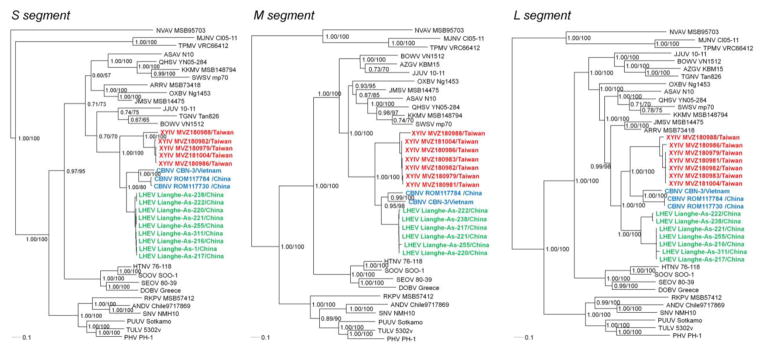
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic trees were generated by maximum-likelihood and Bayesian methods, using the GTR+I+Γ model of evolution, based on the alignment of the S-, M- and L-segment sequences of hantavirus strains. Since tree topologies were very similar using RAxML and MrBayes, the trees generated by MrBayes were displayed. The phylogenetic positions of Cao Bang virus (CBNV CBN-3, S: EF543524, M: EF543526, L: EF543525) and CBNV ROM117784 (S: KJ162406, M: KJ162397, L: KJ162404) and CBNV ROM117730 (S: KJ162407, L: KJ162405) (blue) are shown in relationship to Xinyi virus (XYIV) (red) and Lianghe virus (LHEV) (green). GenBank numbers for XYIV and LHEV are provided in Table 1. Also shown are the phylogenetic positions of Nova virus (NVAV MSB95703, S: FJ539168, M: HQ840957, L: FJ593498), Thottapalayam virus (TPMV VRC66412, S: AY526097, M: EU001329, L: EU001330), Imjin virus (MJNV Cl05-11, S: EF641804, M: EF641798, L: EF641806), Seewis virus (SWSV mp70, S: EF636024, M: EF636025, L: EF636026), Kenkeme virus (KKMV MSB148794, S: GQ306148, M: GQ306149, L: GQ306150), Ash River virus (ARRV MSB 73418, S: EF650086, L: EF619961), Jemez Springs virus (JMSV MSB144475, S: FJ593499, M: FJ593500, L: FJ593501), Qian Hu Shan virus (QHSV YN05-284, S: GU566023, M: GU566022, L: GU566021), Tanganya virus (TGNV Tan826, S: EF050455, L: EF050454), Azagny virus (AZGV KBM15, S: JF276226, M: JF276227, L: JF276228), Jeju virus (JJUV 10–11, S: HQ834695, M: HQ834696, L: HQ834697), Bowé virus (BOWV VN1512, S: KC631782, M: KC631783, L: KC631784), Asama virus (ASAV N10, S: EU929072, M: EU929075, L: EU929078), Oxbow virus (OXBV Ng1453, S: FJ5339166, M: FJ539167, L: FJ593497) and Rockport virus (RKPV MSB57412, S: HM015223, M: HM015219, L: HM015221). Also shown are representative Murinae rodent-borne hantaviruses, including Hantaan virus (HTNV 76–118, S: NC_005218, M: Y00386, L: NC_005222), Soochong virus (SOOV SOO-1, S: AY675349, M: AY675353, L: DQ056292), Dobrava virus (DOBV Greece, S: NC_005233, M: NC_005234, L: NC_005235), Seoul virus (SEOV 80–39, S: NC_005236, M: NC_005237, L: NC_005238); Arvicolinae rodent-borne hantaviruses, including Tula virus (TULV 5302v, S: NC_005227, M: NC_005228, L: NC_005226), Puumala virus (PUUV Sotkamo, S: NC_005224, M: NC_005223, L: NC_005225) and Prospect Hill virus (PHV PH-1, S: Z49098, M: X55129, L: EF646763); and Neotominae rodent-borne hantaviruses, Sin Nombre virus (SNV NMH10, S: NC_005216, M: NC_005215, L: NC_005217) and Andes virus (ANDV Chile9717869, S: NC_003466, M: NC_003467, L: NC_003468). The numbers at each node are posterior node probabilities (left) based on 150,000 trees implemented in MrBayes and rapid bootstrap values (right) based on 100 replicates executed on the RAxML BlackBox webserver, respectively. The scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.