Figure 3.
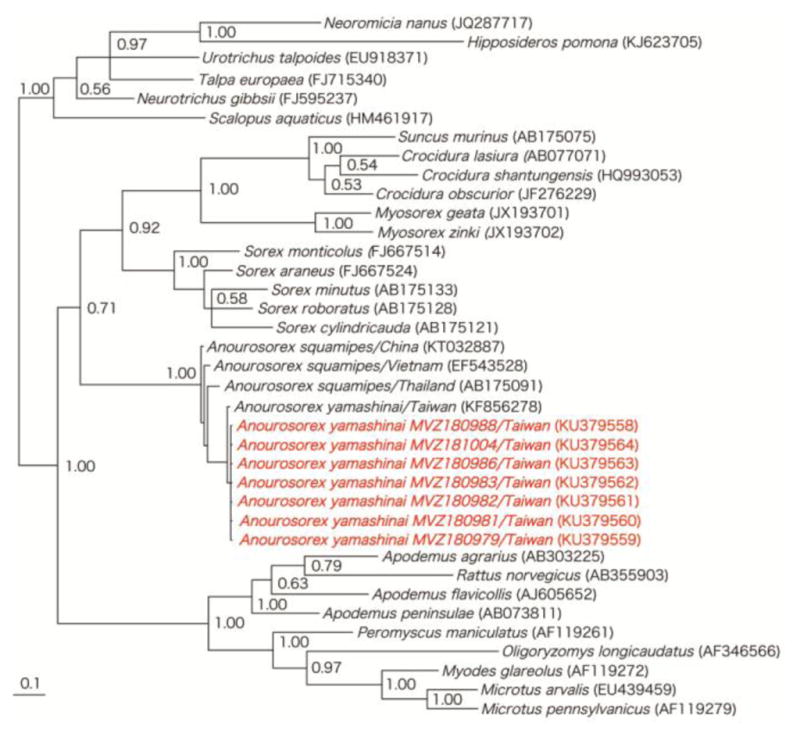
Unrooted phylogenetic tree, using Bayesian method, based on 551- to 1140-nucleotides of the cytochrome b mtDNA of rodents, shrews, moles and bats known to harbor hantaviruses. GenBank accession numbers for cytochrome b mtDNA sequences of Anourosorex yamashinai MVZ180979, MVZ180981, MVZ180982, MVZ180983, MVZ180986, MVZ180988 and MVZ181004 and of other taxa are shown on the tree. Numbers at nodes indicate posterior probability values based on 150,000 trees: two replicate Markov chain Monte Carlo runs, consisting of six chains of 10 million generations each sampled every 100 generations with a burn-in of 25,000 (25%).
