Fig. 1.
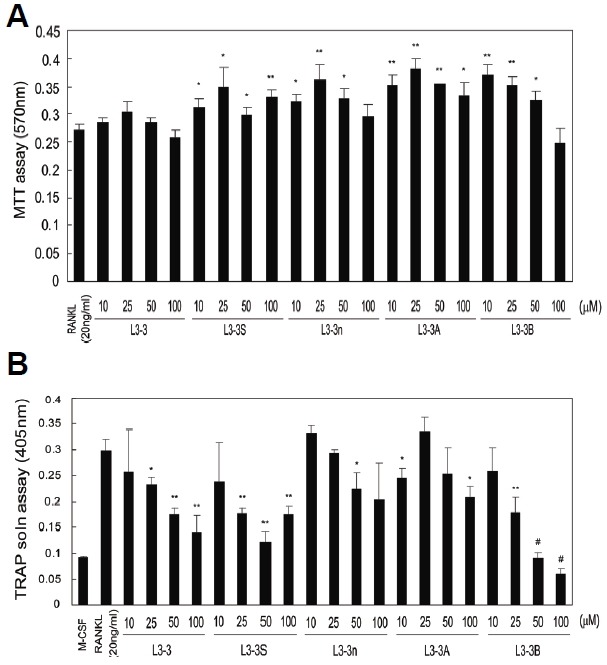
Cytotoxic and inhibitory activities of RANKL-binding peptides. (A) Cytotoxicity of RANKL-binding peptides was estimated by MTT assay. Data represent the mean ± SD of triplicate samples. Results are representative of at least three independent sets of similar experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005 vs. RANKL (20 ng/ml). (B) The inhibition of RANKL-induced differentiation of osteoclasts was examined by TRAP-activity assay. Mouse osteoclast precursors were treated with 20 ng/ml RANKL and varying concentrations (10–100 μM) of peptides. Data represent the mean ± SD of triplicate samples. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; #p < 0.0005 vs. RANKL (20 ng/ml).
