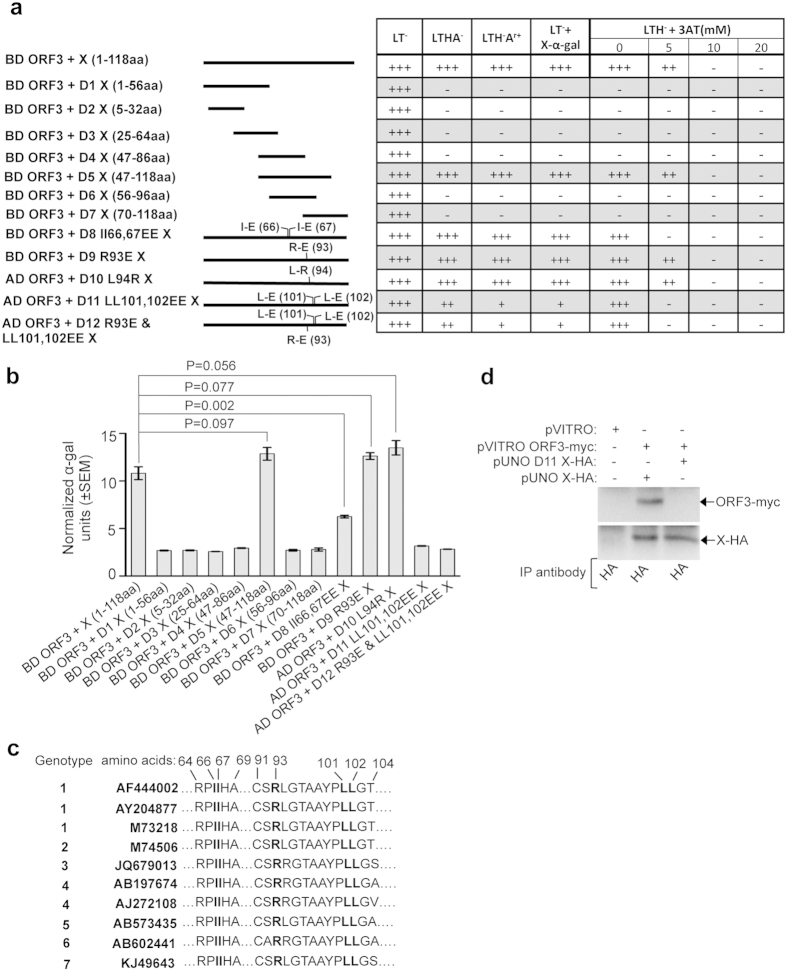
Figure 3. Deletion and point mutation analyses of the X-domain residues responsible for its interaction with the ORF3 protein.
(a) Y2H analyses of the interaction potential of various deletion and point mutants of X with full length ORF3. Length of the deletion mutants is graphically represented as solid lines and amino acid position of point mutants are indicated in brackets. AD: Activation domain, BD: Binding domain, +++: Strong growth, ++: Moderate growth, +: Poor growth, −: No growth, L: Leucine, T: Tryptophan, H: Histidine, A: Adenine hemisulfate, Ar: Aureobasidin, “−”: Deficiency in the medium, “+”: Supplemented in the medium. (b) Quantitative α-galactosidase assay of Y2H gold transformants represented in Fig. 3a. Normalized α-galactosidase units are plotted as ± SEM of triplicate samples. (c) Alignment of X-domain sequence of different HEV isolates. Isoleucine 66th, 67th, Arginine 93rd and Leucine 101st, 102nd are indicated in bold letters. (d) CoIP of Huh7 cell extract expressing empty vector or wild type X (X-HA) and ORF3 (ORF3-myc) or LL-EE mutant X (D11 X-HA) and ORF3 (ORF3-myc), immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibody and immunoblotted using anti-myc (upper panel) or anti-HA (lower panel) antibodies.