Figure 4. rTcMVK adheres to HeLa cells and modulates parasite invasion.
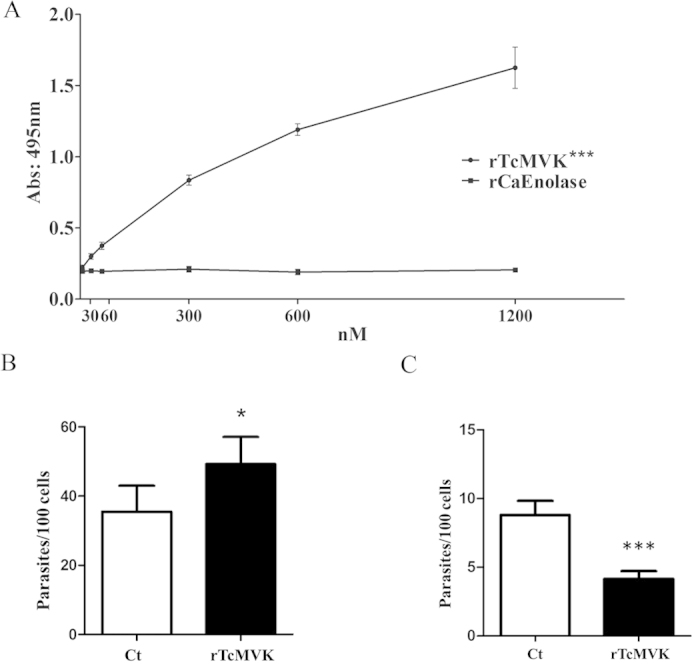
(A) Binding of rTcMVK on the HeLa cells. Paraformaldehyde fixed HeLa cells were incubated with increasing concentrations (nM) of rTcMVK (circle). As a His-tag negative control, HeLa cells were also incubated with rCaEnolase (square), a His-tag recombinant protein from Candida albicans that does not adhere to HeLa cells. This result is the mean of two independent experiments performed in triplicates ± standard deviation (SD). ***P < 0.001. Statistical analysis was performed by Two-way ANOVA method. (B,C) Opposite effects of rTcMVK in the cell invasion by EAs and MTs. rTcMVK enhances EA (B) but inhibits MT invasion (C). Giemsa staining of HeLa cells treated for 1 h with 300 nM of rTcMVK and incubated with EAs or MTs for 2 h. The multiplicity of infection was 10:1 or 20:1 for EA and MT forms, respectively. The negative control was carried out in the absence of rTcMVK. X axis: rTcMVK treated (rTcMVK) and non-treated (Ct) groups; Y axis: percentage of internalized parasites. The data correspond to the mean of six experiments performed in triplicates ± SD. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. Statistical analysis was performed by Student t test method.
